If you take the time to dig beneath the surface of any human community, no matter how humble, you’ll be rewarded with a welter of fascinating tales and characters. Certainly this is true of Oakhurst, California. The little town nestled in central California’s Yosemite Valley near the western end of the Sierra Nevada Mountains has attracted more than its fair share of dreamers and chancers over the past 175 years or so.
Oakhurst sprang up under the name of Fresno Flats back in the 1850s, when, according to the received wisdom back East, the streams of this part of California glittered with gold; one only had to dip a hand in and scoop one’s fortune out. Needless to say, that was not really the case: the vast majority of the starry-eyed prospectors who passed through the budding settlement found only hardship and disillusionment in the forest around it. The people who did best from the gold rush were those who never ventured any farther into the wilderness than Fresno Flats itself, the ones who settled down right there to serve the needs of the dreamers, by selling them picks, axes, shovels, and pans, not to mention food, liquor, beds, and companions to share said beds for a brief spell of a night. Other hardy pioneers later opened a school, a post office, a lumber mill (complete with a log flume on the Fresno River), and eventually even a proper, moderately productive goldmine. Every one of the brave souls who came to the town and stayed had a unique story to tell, but for sensation value none can top that of Charley Meyers.
On the evening of May 22, 1885, two masked men armed with pistols and shotguns robbed a Wells Fargo stagecoach passing through the Yosemite Valley. The sheriff was at a loss about the crime and its perpetrators until the next afternoon, when a local man noticed some footprints leading away from the site of the robbery through the forest — leading, as it happened, directly to Fresno Flats and then right up to the front porch of Charley Meyers, a young farmer and handyman whose family had heretofore been held in good repute. Called to the scene by the amateur sleuth, the sheriff and his deputies burst into Meyers’s log cabin, where they found another resident of the town, a fellow named William Prescott, fast asleep in bed, looking like he had had quite a night. Prescott told the lawmen that Meyers had gone to Coarsegold, the closest town to Fresno Flats. He was duly rounded up there in short order.
The sheriff thought he had his quarry dead to rights. Not only had they left a trail through the woods obvious enough for his half-blind grandma to follow, but their frames matched the victims’ descriptions of their attackers’ build and they were found with guns in their possession that matched the ones used at the robbery. The victims had said that their assailants had smeared boot blacking over all of their exposed skin to further conceal their identity; sure enough, a can of the stuff was found in Meyers’s barn, traces of the same substance on two shirts that had been left lying on the floor inside the house. Further, one of the robbers had been so impolitic as to call the stagecoach driver by his name, indicating that he had to be a local who knew the man. Meyers and Prescott’s claim that they had gone into the woods that night merely to hunt wild hogs fell apart when they were asked to lead their interrogators to their supposed hunting ground separately, and each proceeded to go to a completely different place.
But, once taken to the larger city of Fresno to stand trial, these two rather astonishingly inept criminals were fortunate enough to enlist the services of a rather astonishingly wily defense attorney. Walter D. Grady was a scion of double-barrelled frontier justice straight out of a Zane Gray novel, a hard-drinking brawler who had lost an arm during a shootout. In addition to being a lawyer, he was a California state senator, a goldmine owner, and the proprietor of Fresno’s opera house.
Five years earlier, the transportation arm of the Wells Fargo conglomerate had hired Grady to help it secure the conviction of a different accused robber. But after that task had been accomplished, Grady’s client agreed to pay him only half of the amount he billed it. From that moment on, Walter Grady regarded Wells Fargo as his sworn enemy, making it known near and far that he would happily become the pro bono legal representative of anyone who got sideways with the nineteenth-century mega-corp. For he regarded his feud as a matter of personal manly honor; mere questions of guilt and innocence became less important in the face of such a consideration as this.
As the representative of Charley Meyers and William Prescott, Grady embarked on a strategy of legal exhaustion that Johnnie Cochran would have recognized and nodded along with. He refused to concede even the most trivial of points to the prosecution, even as he scored repeated laughs from the jury with his folksy manner, ribald jokes, and sheer pigheadedness in the face of common sense. For example, he noted that the can of boot blacking found in Meyers’s barn could also be found in those of dozens of other people, and speculated that the traces of the same substance found on the defendants’ shirts might just be residue from “the perspiration of a hard-working man.” (“I never worked hard enough to know,” quipped the sheriff, no stranger to folksy charm himself, by way of response.)
Despite Grady’s legal and logical contortions, Meyers and Prescott were found guilty and sentenced to twenty years at San Quentin State Prison. But their defense attorney refused to give up the fight even now. He appealed all the way to the California Supreme Court, with whom he shared damning evidence that the sheriff and the prosecution team had taken the jury out for drinks on at least two occasions. (He neglected to mention that he had done the same thing himself once.) The conviction was overturned and the prisoners remanded for a new trial. Grady did his thing, and this time he was able to charm or flummox enough of the jury to secure a mistrial. A third trial was ordered; another mistrial followed. By this point, the case had become a running joke in Fresno and its surroundings, with Grady, Meyers, and Prescott becoming unlikely folk heroes for the way they kept fighting the law and common sense and, if not quite winning, at least staving off defeat again and again. The authority figures who had been cast in the roles of the straight men in this legal farce decided they had had enough; they vacated the case and let the prisoners go free. You win some, you lose some.
So, Meyers and Prescott came home to Fresno Flats about a year and a half after they had been led away in handcuffs. Justice may not have been served, but Charley Meyers at least seemed to have been scared straight by his brief sojourn in San Quentin. He worked hard at legitimate pursuits, married well, and became a prominent landowner and businessman in his community. Throughout, he refused as adamantly as ever to fess up to being one of the perpetrators of the stagecoach robbery of 1885. Yet people in Fresno and elsewhere continued to remember him and the town from which he hailed primarily for that bizarre series of trials and his improbable escape from justice.
This really stuck in the craw of his wife Kitty Meyers, an eminently respectable lady. She decided that, if only a town called Fresno Flats no longer existed, people might stop talking about her and her husband in this unsavory context. She therefore embarked upon a lengthy campaign with the post office to change the official name of the town, a campaign whose ultimate success was more a testimony to apathy among her fellow residents than any groundswell of support for the idea. On April 1, 1912, Fresno Flats became Oakhurst in the eyes of the post office and the rest of the government. For many or most of the residents of the town, however, it would remain Fresno Flats for decades to come.

Charley and Kitty Meyers, long after the former had put his stagecoach-robbing days behind him. If Kitty hadn’t gotten tired of hearing her husband’s name brought up in association with that crime, Sierra On-Line’s boxes would have listed Fresno Flats rather than Oakhurst as the company’s address 70 years later. When a butterfly flaps its wings…
By whatever name, the town was still, as a report in the closest newspaper delicately put it, a “lively” place at this time, filled with miners and lumberjacks whose interests and recreations weren’t all that far removed from those of the starry-eyed prospectors the place had first been built to serve. (“One of the major sports among men at payday was pitching $20 gold pieces to a wagon rut. [The] man pitching the closest took all the coins on the ground.”) In time, though, the local goldmine ran out of bounty from the earth, and in 1931 the onset of the Great Depression spelled the end of the lumber mill as well. “Now, like so many of the early mountain towns, Fresno Flats finds itself slowly rotting away, soon to become another of the ghost towns of the Sierras,” wrote its last remaining schoolteacher despairingly in 1938.
But this mountain town got a new lease on life before it rotted away completely. In the 1950s, automobiles and the new interstate highway system led to an explosion in the number of visitors to this region of incredible natural beauty. Fulfilling at long last the ambition of the now long-dead Kitty Meyers by shedding the name of Fresno Flats once and for all, Oakhurst reinvented itself as “The Gateway to Yosemite National Park.” Road-tripping families became a more lucrative and far more reliable source of revenue for Oakhurst businesses than the gold hunters of yore had ever been.
Yet just like back then, some minuscule percentage of the visitors who streamed through the town elected to stay and leave their mark upon it. They were people like Jack Gyer and Cal Ragland, a pair of Los Angelenos who started the Sierra Star, the town’s first and only newspaper, in 1957, when there were still just 85 telephone numbers in all of Oakhurst. And they were people like the Ohioan Hugh Shollenbarger, who in 1965 erected the optimistically titled “World Famous Talking Bear” on Highway 41 just at the edge of Oakhurst. In the decades since, this statue of a grizzly bear has growled and spouted facts about his species from a tape recorder ensconced somewhere inside his fiberglass innards to thousands upon thousands of tourists, winning himself a page in many a catalog of roadside American kitsch. (“I am a native of this area, but don’t be alarmed. There are not many of us left…”)

The World Famous Talking Bear in Oakhurst. Notice the name on the storefront just behind him. Century 21 Real Estate was one of the brands owned by HFS, then later by Cendant Corporation. It’s a small world sometimes…
Seen in the light of this long tradition of creative entrepreneurship, Ken and Roberta Williams’s decision to move the “headquarters” of their budding two-person company On-Line Systems to Oakhurst in December of 1980 begins to seem like less of an aberration — even if, as I wrote quite some years ago now in these histories, Oakhurst was “about the unlikeliest site imaginable for a major software publisher.” They bought a home in Coarsegold, the neighboring town where Charley Meyers had been apprehended all those years ago, and leased their first office space in Oakhurst proper, in the form of a tiny ten-foot-by-ten-foot room above the print shop where new issues of the Sierra Star were run off each week. Indeed, the name of their early newspaper landlord may very well have been a factor in the Williamses’ decision to rechristen their company “Sierra On-Line” within a couple of years.
Like so many of those who had come to Oakhurst before them, Ken and Roberta Williams arrived seeking financial success; Ken, you’ll recall from the first article in this series, wanted more than anything else in life simply to become rich. Yet they both wanted to attain success on their own terms, in a town surrounded by all the trappings of paradise; their dream was half Ayn Rand, half Robert M. Pirsig. But first, like Charley Meyer before him, Ken Williams in particular had to go through a bit of an outlaw phase, filled with wild parties and a fair amount of recreational drug use and even a modicum of libertine sex, before he straightened up and turned Sierra into a respectable company. The tales about how he did that, and of a goodly number of the hundreds of games said company published over its nearly sixteen years of independent existence, have been a regularly recurring fixture of these histories of mine almost since the very beginning. So, rather than attempt to summarize them here, allow me to point you to the hundreds of thousands of words I’ve already written on these subjects.
As these tales were playing out, Oakhurst was being invaded by a new breed of outsider: folks who tended to be somewhat paler and skinnier than the legions of road-trippers and hardcore hikers streaming through, folks who tended to talk an awful lot about kilobytes and registers and opcodes and other incomprehensible technical arcana. The locals shrugged their shoulders and accepted them, as they had so many other strangers in the past. After all, their money spent just as well as anyone else’s at restaurants, shops, and gas stations, and some of them seemed to have a considerable amount of it to throw around. For their part, some of the computer-mad newcomers learned to love their new lives here in paradise, a few of them to such an extent that they would do their darnedest to avoid leaving it, even after the job that had brought them here was no more.
For to everything there is a season — to computer-game publishers just as to everything else, in Oakhurst just as everywhere else. The first indubitable sign that Sierra On-Line’s season in Oakhurst might not be eternal emerged already in 1993, when Ken and Roberta Williams set up a second office for the company in Bellevue, Washington, not far from Microsoft’s sprawling campus, to serve as its new “administrative headquarters.” By now, Ken was no longer the genial, party-hearty boss who had once celebrated the end of the working week each Friday by slamming down schnapps shots with his staff. The more buttoned-down version of Ken Williams insisted that the office in Bellevue was necessary. He said — and we have no reason to doubt his word on this — that Sierra’s isolated location was making it hard for him to hire top-flight talent from the world of business and finance, that Oakhurst’s lack of proximity to a major airport was becoming a crippling disadvantage in an ever more competitive, increasingly globalized industry. Nevertheless, in a telling testament to how big the gap between the Williams family and the rank and file in Oakhurst was already becoming, some of the latter believed the decision to up stakes for Bellevue was an essentially personal one, having much to do with the absence of a state income tax in Washington. And who knows? That may very well have been a consideration as well. For whatever reason or reasons, the era of a collective of “software artisans in the woods” effectively ended for Ken and Roberta Williams in 1993.
Although the announced plan was to continue to make the games in Oakhurst and to market them from Bellevue, many of the established staff suspected that this division of labor would prove no more than temporary. Sierra game designer Corey Cole, for one, told me that he was “pretty sure that the move would soon result in moving most or all of the project teams out of Oakhurst.” His cynicism was partially validated just one year after the Bellevue office opened, when Sierra laid off a substantial chunk of the Oakhurst workforce, in the most brutal downsizing of same since the company had nearly gone bankrupt in the wake of the Great Videogame Crash of 1983. Sure enough, Bellevue now started making games as well as selling them. In fact, as the Oakhurst employees saw it, Ken Williams now displayed a marked tendency to choose the projects that he felt had the most potential for his own backyard, leaving the scraps to the town that had built Sierra. Be that as it may, one definitely didn’t need to be a complete cynic by this point to suspect that the writing was on the wall for Sierra’s remaining software artisans in the woods.
Thus when the news came down to Oakhurst from Bellevue a year and a half after the traumatic layoff that Sierra On-Line had been suddenly, unexpectedly acquired by a company called CUC, it was greeted with more trepidation than excitement. The Oakhurst people’s first question was the obvious one: “Who the hell is CUC?” Craig Alexander, the current manager of the Oakhurst operation, was less surprised that Sierra had been acquired — he had always suspected that to be Ken Williams’s endgame — than he was by the acquirerer. “We always thought we’d be bought by a large media concern or Hollywood studio or technology company,” he says. A peddler of borderline-reputable shopping clubs and timeshares had not been on his bingo card. Al Lowe of Leisure Suit Larry fame saw dark clouds on the horizon as soon as he read the email from CUC that said, “We love this company. That’s why we bought it.” “Translated into English,” Lowe says wryly, “that means, ‘We’re going to change everything.'”
In the long run, his prediction wouldn’t be wrong, but there was a period when the more optimistic folks in Oakhurst were given enough space to fondly imagine that their lives might continue more or less as usual indefinitely. The Sierra employees who lost their jobs in the immediate aftermath of the acquisition were the marketers, accountants, and other front-office personnel who worked from Bellevue, who were deemed redundant after it became clear that Bob Davidson and his administrative staff rather than Ken Williams and his would be setting the direction of the new CUC software arm. The Oakhurst people sympathized with the plight of their ostensible comrades in arms, but the truth was that there had been little day-to-day contact between the two halves of the company — and, what with the stresses and rivalries playing out in the corporation as a whole, not always a lot of love lost between them either.
Still, there were some changes in Oakhurst as well, some of which become distinctly ominous in retrospect. “Little conversations stick out” today in the memory of Craig Alexander: “I remember CUC management lecturing me and my leadership about why we couldn’t deliver revenue and earnings on a quarterly basis. They were all proud of the fact that they had been delivering to Wall Street expectations for the last four or five years. ‘How come you guys can’t do that?'” CUC called everyone in Oakhurst together to pitch to them a scheme known as “salary replacement,” in which employees would agree to be paid partly in stock rather than cash; a fair number of them signed up, much to their eventual regret. Less sketchily but no less disturbingly, the Oakhurst folks were told that they now worked at “Yosemite Entertainment,” just one of a portfolio of studios that would henceforward live under a broad umbrella known as Sierra. To be thus labeled just one among many sounded worrisomely close to being labeled expendable.
For the time being, though, games continued to be made in Oakhurst. One of these would prove the very last of the “Quest”-branded Sierra adventure games, released about two weeks after King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity wrapped up another such series in such confusing and dismaying fashion. Quest for Glory V: Dragon Fire would acquit itself decidedly better, even though it too was subject to many of the same pressures that conspired to so thoroughly undo Mask of Eternity. As was always the case with the Quest for Glory series, its ability to at least partially defy the natural gravity of Sierra, where good design was never a thoroughgoing organizational focus even in far less unsettled times than these, was a tribute to Corey and Lori Ann Cole, to my mind the two best pure game designers who ever worked on Sierra’s adventure games.
In a way, the most remarkable thing about Quest for Glory V is that it ever got made at all. Certainly no reasonable person would have bet much money on its chances a short while after the fourth game in the Coles’ series of adventure/CRPG hybrids came out.
That entry, Quest for Glory: Shadows of Darkness,1 is considered by many fans today to be the very best of them all. Yet the game that modern players experience through facilitators like ScummVM is not the same as the one that was released on December 31, 1993, just in the nick of time to book its revenues as belonging to the third quarter of Sierra’s Fiscal 1994. The game as first shipped was riddled with bugs and glitches that led to harsh reviews and many, many returns. Although some of the worst of the problems were later remedied through patches, the damage had been done: Shadows of Darkness’s final sales figures were not overly impressive. The Coles were contractors rather than employees of Sierra at the time they made it, but they too felt the pain of the layoff of 1994. The day after more than 100 regular employees had gotten their pink slips, Ken Williams met with them to tell them that there would be no Quest for Glory V. The series, it seemed, was finished, one game short of the epic finale that the Coles had been planning for it ever since embarking on the first installment circa 1988.
I mentioned earlier that some of the people who came to Oakhurst to work at Sierra never left the town even after the job that had brought them disappeared. Count Corey and Lori Ann Cole among this group. Even though their services were no longer desired at Sierra, they were determined to keep on living here in paradise. They took on contracting projects that they could do from their home, most notably the adventure game Shannara for Legend Entertainment, based on the long-running series of fantasy novels by Terry Brooks.
Some time after that game came out — and after a second game for Legend, to be based on Piers Anthony’s Xanth novels, had fallen through — a rapprochement between the Coles and Sierra took place. One of the projects that was still being run out of Oakhurst was The Realm, one of the first graphical MMORPGs, which ran on a modified version of Sierra’s venerable SCI adventure engine and even lifted some of its code straight from the Quest for Glory games — understandably so, given that these were the only other SCI games which, like The Realm, weaved monster-killing, character levels and stats, and other CRPG traits into their tapestry of adventure. For a while, Craig Alexander considered turning The Realm into some sort of Quest for Glory Online with the help of the Coles, but ultimately thought better of it.
Nonetheless, the lines of communication had been reestablished. Sierra had received a good deal of fan mail over the last couple of years asking if and when the next Quest for Glory would come out; the fourth game had ended on a cliffhanger, which only made the fans that much more desperate to know how the story ended. So, it did seem that there was a market for a Quest for Glory V, even if a relatively small one by the standards of the growing industry. Hedging his bets in much the same way that Roberta Williams was about to do with King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity, Craig Alexander came up with the idea of a “small-group multiplayer” game; a matchmaking service would put players together in “shards” with just a handful of others, as opposed to the hundreds or thousands who could play together in The Realm. Yet it was never clear how the narrative focus of the older Quest for Glory entries might be made to work under such a conception. Lori Ann Cole accepted a commission to work up a design, but she almost immediately began lobbying for the inclusion of a single-player mode as well. This, one senses, is where her heart really was right from the start: giving players the narrative closure they were begging for in all those letters. Under the pressure of practicalities, the multiplayer aspect gradually slid away, from being the whole point of the game to an optional, additional way to play it; then it disappeared entirely in favor of a Quest for Glory like the series had always been, in the broad strokes at least.
Still, Quest for Glory V was destined to remain the odd man out in the series in many other, more granular respects. The SCI engine wasn’t maintained after 1996 — The Realm was one of the last things ever done with it — and so the team behind the fifth game was forced to look for another way of implementing it. Lead programmer Eric Lengyel first devised a state-of-the-art voxel-graphics system, only to find that it was too demanding for the hardware of the day. After some flailing against the inevitable, he agreed to scrap it and code up a more conventional 3D-graphics engine from scratch. Corey Cole, who didn’t join the project until it was about a year old, considers all of these efforts to have been misplaced. Buying someone else’s 3D engine would have entailed a large one-time cost, he notes, but it would have freed up a lot of time and energy to focus on design rather than technicalities. He has a point.
During 1998 and 1999, the new-look Sierra would release three adventure games with one foot in the past and one in the future: King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity, Quest for Glory V: Dragon Fire, and Gabriel Knight 3: Blood of the Sacred, Blood of the Damned (a subject for a future article). Rather incredibly, each of these games would run in a different 3D engine, two of them custom-built for this application and then never used again. The contrast with the 2D SCI engine, which was used over and over again in dozens and dozens of applications, could hardly be more stark. It seems that there are major advantages to having a group of developers all working out of the same location and communicating daily with one another, as was the case during the glory days of Sierra in Oakhurst. Who would have imagined?
Of the three aforementioned games, Quest for Glory V is the only one that could have been implemented in 2D without losing much if anything. Despite the departure from the comfortable old SCI environment, its presentation and gameplay are quite consistent with that of the earlier games in the series: that of a (mostly) fixed-camera, mouse-driven, third-person graphic adventure of the classic style, with a geography divided into discrete areas or “rooms.” Combat is a little different from before, in that it takes place on the same screen as the rest of the gameplay, but, again, it’s hard to see why this couldn’t have been implemented in SCI. The benefits of 3D graphics, such as they were, must have come down largely to the production costs they could save — although one does have to question how much money if any was really saved in the end, given the time and effort that went into making a 3D engine from scratch, such that Quest for Glory V ended up becoming by far the most expensive of all the games in the series. On the plus side, though, the visuals are generally sharp, colorful, and reasonably attractive; they’ve held up a darn sight better than many other examples of 1990s 3D. From the player’s perspective, then, the choice between 2D and 3D is mostly a wash.
In other respects, Quest for Glory V has a lot going for it. Each game in the series before it has a setting drawn from the myths and legends of a different real-world culture: Medieval Europe for the original Quest for Glory, the tales of the Arabian Nights for Quest for Glory II: Trial by Fire, Sub-Saharan African and Egyptian mythology for Quest for Glory III: The Wages of War, Gothic Transylvania (plus an oddly discordant note of H.P. Lovecraft) for Quest for Glory: Shadows of Darkness. Quest for Glory V: Dragon Fire is based on ancient Greek myth, a milieu more familiar to most Western gamers than any since that of the first game. The Coles take their usual care to depict the culture in ways that combine humor, excitement, and respect. And in the end, who isn’t happy at the prospect of spending some time on a sun-kissed Aegean archipelago? Quest for Glory V is a nice virtual place just to inhabit, which is a large part of the battle in making a satisfying adventure game.
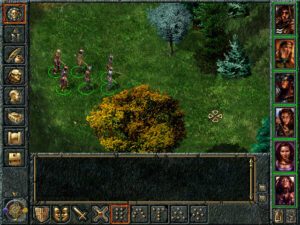
Another large part is the gameplay itself, of course, and here as well Quest for Glory V acquits itself pretty well. The puzzles are generally solid. The combat is more frequent and more action-oriented than in the earlier games, betraying more than a slight influence from the hugely popular real-time-strategy genre, but the shift is more one of degree than of kind. At its best, Quest for Glory V, like its predecessors, manages to avoid that sense of jumping through arbitrary hoops that dogs so many adventure games, making you feel instead like you’ve been plunked down at the center of an organically unfolding story. This isn’t always the case, mind you; there are a few puzzles that are under-clued in my opinion, such that the grinding gears of the game show through when you encounter them and have your progress stopped dead. But by any objective standard, there’s more to like than dislike about the design of Quest for Glory V.
For all that, though, I must admit that I walked away from the game feeling a little bit underwhelmed — and, judging from what I’ve read of other players’ reactions, that feeling is fairly typical. There’s an elegiac quality to Quest for Glory V that overshadows the here-and-now plot, involving, it eventually emerges, a dragon who is ravaging the archipelago by night. The Coles indulge in buckets and buckets of fan service, bringing back characters who were both prominent and obscure in the previous games, for starring roles and cameos in this one. Nice as it is to see them, the Greekness of the setting sometimes threatens to get lost entirely amidst this multicultural babble. It’s a double-edged sword for which I can’t prescribe any ready remedy. For a fan who grew up with Quest for Glory, seeing characters from childhood memory return like this must have been magical indeed. For fans who grew up with Sierra’s adventure games in general, and were now beginning to suspect that there were not likely to be many more such games, the poignancy must have been that much more intense — as if all of these beloved characters were waving farewell not just to this gaming series, but to an entire era of gaming history.
That said, the constant nostalgic callbacks do have a way of preventing Quest for Glory V from ever fully standing on its own two feet, separate from the series for which it serves as the finale. Even those players whose eyes filled with tears upon seeing the wise old leonine paladin Rasha Rakeesh on their monitor screens again might have to admit that the game never quite feels like the epic culmination of all that has come before which it perhaps ought to be; throughout its considerable length, it feels rather more like The Lord of the Rings after Frodo has thrown the One Ring into Mount Doom. In one sense, that’s noble, moving as it does beyond the lizard-brain emotional affect of most games. But it does also demonstrate that, although Quest for Glory V is a vastly better game than King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity by any standard you care to name, it was nevertheless subject to some of the same cognitive dissonances. There weren’t enough old Quest for Glory players to justify its budget, even as the new players that the better graphics and more extensive and action-oriented combat were meant to attract would feel like they had been invited to a cocktail party where everyone knew each other and they didn’t know anybody.
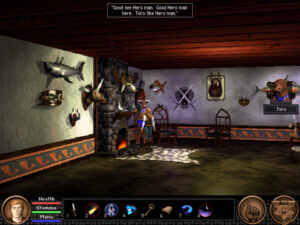
Despite the technological changes, Quest for Glory V still looks and feels like a Quest for Glory. The Adventurer’s Guild here looks much like the one in the first game, except that it’s now filled with mementos of your own previous adventures.
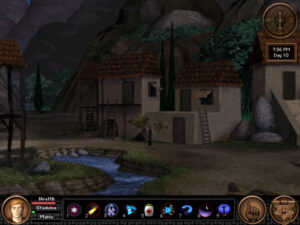
In addition to looking like Quest for Glory, the game also manages to look appropriately Greek. And note the time that is displayed at the upper right. Like all of the other games in the series, Quest for Glory V plays in accelerated real time, complete with day-to-night cycles. This can be annoying in that you have to keep going back to your hotel room to eat and sleep, but it does wonders for the verisimilitude of the experience.
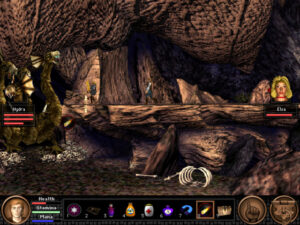
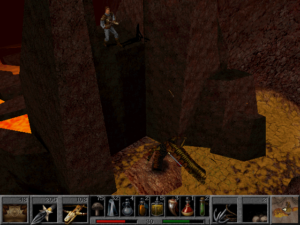
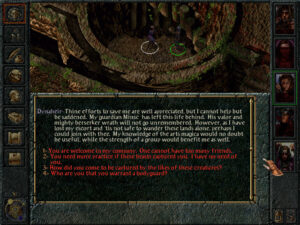
Fighting a hydra with your old friend Elsa, whom you first met all the way back in the first game, where you freed her from Baba Yaga’s curse. In another blast from the past, the Quest for Glory V combat engine was the work of John Harris, one of Ken Williams’s star programmers from the very early days, the creator of a masterful clone of Pac-Man. As chronicled at almost disturbing length in Steven Levy’s classic book Hackers, Ken Williams made it his mission in life for a while to get the shy and awkward young man laid. The version of John Harris who returned to work on this game was presumably more worldly…
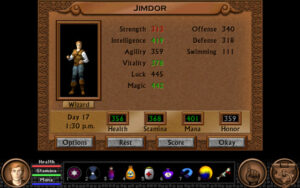
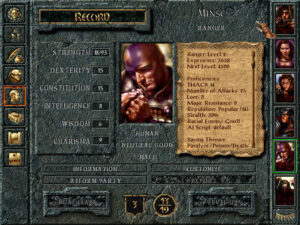
You can take the same character through all five Quest for Glory games, which is kind of amazing when one considers the transformative changes in computer technology that took place over the decade or so that the series encompassed. And yet Quest for Glory V doesn’t give you the feeling that your character has become really, really powerful. All of the monsters to be found here are strong enough themselves to challenge him; there are no kobolds to go and beat on to prove how far he’s come. Similarly, if you create a character from scratch, you don’t necessarily feel that this is a high-level character. Is this part of the reason that the game fails to inculcate that elusive sense of being truly epic? Perhaps.
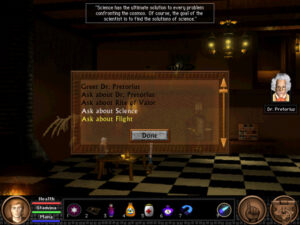
The Science Island section smacks of The Castle of Doctor Brain.
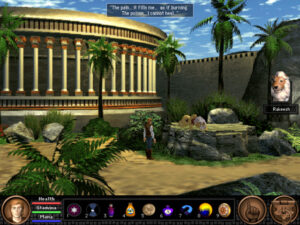
Veterans of the series will be horrified when Rakeesh is poisoned. Newcomers will wonder who the hell this weird lion guy is and why they should care what happens to him. Herein lay many of the game’s problems as a commercial proposition.
Quest for Glory V was released on December 8, 1998, about a year behind schedule. Reviews tended to be on the tepid side. Computer Gaming World’s was typical. “While Quest for Glory V isn’t likely to win over anyone new,” wrote Elliot Chin, “it will serve as a fond farewell for all those longtime fans who want to guide the Hero through one last adventure”; he went on to admit that “what fueled my desire to play the game was nostalgia.” Perhaps surprisingly in light of reviews like this one, Corey Cole believes it may have sold as many as 150,000 copies, although a substantial portion of those sales were probably at a steep discount as bargain-bin treasures.
If you had told the people in Oakhurst on the day that Quest for Glory V shipped that it would be the very last adventure game to come out of their offices, they might have been saddened, but they wouldn’t have been shocked. For it had been announced just eighteen days earlier that Sierra had another new owner, this one based more than a quarter of the way around the world from the Yosemite Valley. The people at Yosemite Entertainment had good cause to feel themselves more expendable than ever.
Did you enjoy this article? If so, please think about pitching in to help me make many more like it. You can pledge any amount you like.
Sources: The books Not All Fairy Tales Have Happy Endings: The Rise and Fall of Sierra On-Line by Ken Williams and Hackers: Heroes of the Computer Revolution by Steven Levy. Computer Gaming World of October 1997 and April 1999; Sierra’s customer newsletter InterAction of Fall 1996, Spring 1997, Fall 1997, and Fall 1998, Sierra Star of November 28 2017; Fresno Bee of March 8 1912; Madera Tribune of September 24 1957 and February 18 1965.
Online sources include “How Sierra was Captured, Then Killed, by a Massive Accounting Fraud” by Duncan Fyfe at Vice, the Fresno Flats Historic Village & Park’s “History of Fresno Flats & Oakhurst,” “Stagecoach to Yosemite: Robbery on the Road” by William B. Secrest at Historynet, and an old television interview with Hugh Schollenbarger.
I also made use of the materials held in the Sierra archive at the Strong Museum of Play. Most of all, though, I owe a debt of gratitude to Corey Cole for answering my questions about this period at his usual thoughtful length.
Where to Get It: All five Quest for Glory games are available for digital purchase as a single package at GOG.com. And be sure to check out Corey and Lori Ann Cole’s more recent games Hero-U: From Rogue to Redemption and Summer Daze: Tilly’s Tale.