Some passions are lifelong, but many others fade away over the course of a life, to be replaced by others. Not long after Jon Van Caneghem, the founder of New World Computing, sold his company to 3DO, it started to become obvious to everyone who worked for him that the torch he carried for computer games no longer burned as brightly as it once had. A younger version of Van Caneghem had spent almost three years designing and programming Might and Magic I, the CRPG that introduced New World to our world, virtually all by himself. Now, he was coming into the office just two or three times a week, leaving even on most of the days when he did make an appearance by shortly after lunchtime. His all-dominating current passion, it was becoming clear, was racing sports cars on tracks all over California and beyond. His colleagues sensed that, in his mind, he had already created his magnum-opus CRPG with Might and Magic IV and V, two big games that could be combined into one to form The World of Xeen, an absolutely massive one. Meanwhile he had poured all of his best strategy ideas into The King’s Bounty and Heroes of Might and Magic. He was ready to take two steps back from the day-to-day at New World, to become a part-time designator emeritus and spend the rest of his time driving his cars.
In due course, Van Caneghem’s disengagement would become a problem for the company, arguably even one of the direct causes of its downfall shortly after the millennium. Right now, though, at the end of the 1990s, there was still sufficient momentum to keep things gliding along reasonably well. In fact, 1999 would become New World’s best year of all in purely commercial terms, being the first with major new releases in both the Heroes of Might and Magic and Might and Magic franchises.
A sequel to a game as successful as 1996’s Heroes of Might and Magic II seemed like a no-brainer by industry logic. And yet New World was oddly nervous about spending too much money on it. For the Heroes games were turn-based experiences with hand-drawn pixel art, in an era when real-time 3D was more and more the rage. Accordingly, Heroes III was handled cautiously, allocated only a limited budget and window of time to come to fruition.
Production began in September of 1997, with the hiring of two key figures. David Mullich, who was to be director and project leader, was a grizzled games-industry journeyman whom we’ve met twice before in the course of these histories, at widely separated intervals: once for his highly experimental 1980 game The Prisoner, an enduring icon of the early Apple II scene, and once for I Have No Mouth, and I Must Scream, the equally uncompromising point-and-click adventure game he made in 1995 with the visionary and infamously irascible science-fiction writer Harlan Ellison. Both of these projects lived well out on the artsy end of a career that also encompassed plenty of less challenging, more straightforward fare. Needless to say, Heroes III would belong more to the latter category than the former. For neither of Jon Van Caneghem’s signature franchises had ever set out to touch hearts and minds in any profound way, just to show their players a good time.
Whereas Mullich had been in the games industry almost since before said industry had existed, the man selected as Van Caneghem’s “co-designer” on Heroes III — in reality, this meant that he was a lead designer subject to his largely absentee boss’s veto power — was a rank beginner. Greg Fulton had never shipped a game before; relatively short stints at Activision and the interactive division of Steven Spielberg’s DreamWorks had culminated only in cancellations, as the industry navigated the shrinking market for multimedia-heavy adventure games and the growing one for 3D-modelled action. Nevertheless, Van Caneghem saw something — perhaps something of his own younger self? — in the games-addled, absurdly enthusiastic twenty-something who turned up for an interview with a notebook full of ideas for where to take the Heroes franchise after the departure of Phil Steinmeyer, Van Caneghem’s previous co-designer. Against all the odds, the kid got the job.
Fulton’s brief was most emphatically not to reinvent a wheel that was still rolling along perfectly well. He was rather to take the game that Jon Van Caneghem had originally designed under the name of The King’s Bounty back in 1990, then expanded upon twice with the help of Steinmeyer to create Heroes I and II, and expand upon it yet one more time by adding more monsters, more treasure, more factions, and whatever else seemed advisable without mucking up the rather brilliant core design. On his side, he fully understood what was expected of him.
We had to use the existing Heroes II engine within a tight window of time. On top of this, we had a passionate fan base who absolutely loved Heroes II, and, for its sequel, didn’t necessarily want a radical departure. I could not play fast and loose with the design of Heroes of Might and Magic III. I needed design evolution, not design revolution. Thus, my overarching guideline for Heroes III became, “If it isn’t in the spirit of Heroes of Might and Magic… kill it.”
So, over the course of seventeen months, Heroes II was transformed into Heroes of Might and Magic III: The Restoration of Erathia. The graphics resolution was bumped up from 640 X 480 to 800 X 600, and the game was given a moodier, more realistic, less cartoon-like look to suit changing aesthetic fashions. The space where tactical combat took place was made about twice as large to allow more room for maneuvering. Scenario designers were given the option of adding an underground level to their overland maps. Two new playable factions were added to the six of Heroes II, and more buildings were made available to construct in each faction’s towns. Each faction got a new unit type as well, and all units instead of just a select few were made upgradable. The heroes who led the armies were allowed to bring up to seven rather than five different types of units with them. More CRPG elements were added to the game, with each hero being given one innate special ability and a wider range of secondary skills to learn. The magic system was expanded, with the spells at the player’s command now divided into separate, elemental schools that magic-oriented heroes had to learn separately.
Half a dozen campaigns were created in lieu of the single one — playable from either side — of Heroes I and II. Not only were these campaigns given more fully fleshed-out story lines — the one that gave the game its subtitle followed directly on from the story of Might and Magic VI — but the individual scenarios that comprised them were given more continuity by allowing players to bring heroes and equipment with them from scenario to scenario. And for those who preferred to play with or against other humans, the networked multi-player mode was given an extra coat of spit and polish.
In short, Heroes III became a case study in smart, evolutionary game design, elaborating on those aspects of its predecessor that seemed to need elaboration — or at least that seemed tolerant of it — whilst leaving the core systems that already worked so well as they were. The overriding intention was that Heroes III should be perfectly comprehensible to any Heroes II player from the moment she fired up her first scenario. This fourth iteration on the same basic design was to be the last word on it.

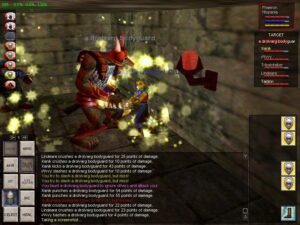
Queen Catherine, the star of the lead Heroes III campaign, appears in the opening movie dressed in a brassiere, chainmail thong, and high heels. She looks more like a pole dancer at a fetish club than a noble queen and warrior.
Thankfully, the rest of the game tones down the horny-adolescent clichés. Veterans of previous Heroes games will feel right at home right away in this interface.
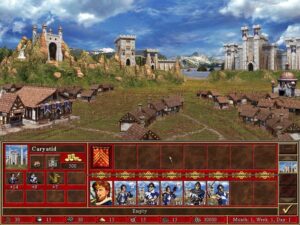
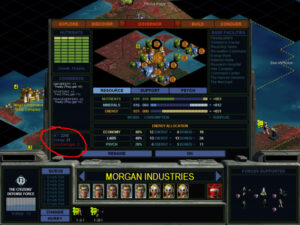
A town waiting to be developed. Certain design choices, such as the addition of trading posts as cheap buildings everywhere, have made gold and other resources easier to come by in the early game, which makes the scenarios play somewhat faster.
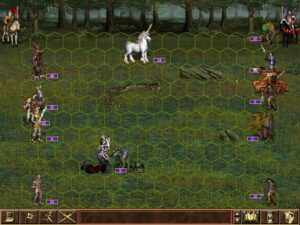
Tactical combat now takes place in a space with four times the quantity of hexes. As a result, most melee attackers can no longer reach ranged attackers on the first turn, altering the balance of power among the units considerably.
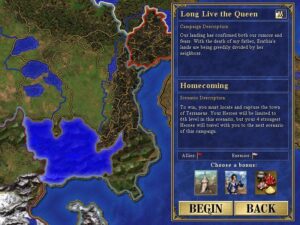
Beginning a new campaign. A lot of effort has been put in to make the campaigns feel less like a string of standalone scenarios and more like a seamless whole. (Alas, the benefits are kind of lost on me. I’m usually a story guy, who goes right for the single-player campaigns. Yet I’ve never been able to work up much interest in Heroes campaigns, having my best fun with single scenarios — especially multi-player ones. Go figure. Maybe it’s just down to Heroes of Might and Magic being among the few games that my wife really wants to play with me instead of just commenting from the sidelines — itself a testament to their broad-based appeal.)
Every Heroes of Might and Magic game made by New World sports an exceptional orchestral soundtrack. Heroes III may have been the first game ever to utilize a newfangled audio-compression format known as MP3, which would ignite an international furor when the Napster MP3-sharing service made its debut later in 1999.
David Mullich and Greg Fulton thoroughly succeeded in their brief by most reasonable standards. Today, Heroes of Might and Magic III is widely regarded as the entry from the franchise to get.
Contrarian that I am, though, I do find that I want to push back against that idea just a little bit. At the end of the day, I actually think that I slightly prefer Heroes II. Part of my preference comes down to raw aesthetics. I like the more cartoon-like, cheerfully goofy graphics of Heroes II better than the more conventionally “gamer dark” visuals of Heroes III; I’ll take Heroes II’s Count Chocula vampires, who unleash a theatrical Bluhhh! every time they attack, over Heroes III’s Nosferatu grotesques any day. I was amused in a “how different people are” sort of way when I read one of Greg Fulton’s recollections about the Heroes III project, saying that he and David Mullich considered “fixing the artwork” to be their most important priority going in, behind only the all-encompassing one of “don’t screw a good thing up.” If you ask me, the fun and frothy Heroes II art has aged ironically better than that of Heroes III. In any of its incarnations, Heroes of Might and Magic is a game to be enjoyed, but never one to be taken too seriously.
Then, too, those of you who’ve been around here a while will know that I tend to be skeptical of strategy-game sequels that simply add more stuff. Mind you, I don’t think that any of the additions to Heroes III ruins the experience; their saving grace is that they tend to add variety rather than turn-to-turn complexity. Fulton was wise enough not to do away with the limit of eight active heroes per player. Presumably a result of technical limitations in the earlier games, it ensures that Heroes III plays snappily, never getting bogged down with dozens of armies in the way that any veteran of late-stage Civilization II or Alpha Centauri will all too readily recognize.
I do think, however, that Heroes III pushes right up the edge of diminishing returns in other areas. The new faction ordering, for example, destroys the lovely symmetry of the two good, two neutral, and two evil factions in Heroes II. Even after playing the game for many hours, I still can’t really keep the Heroes III factions straight in my head. I don’t have that problem with Heroes II.
Still, there is context to these judgments — and I mean that unusually literally in this case. If there’s one thing I’ve learned over the years I’ve been writing these histories, it’s how well-nigh impossible it is to separate our judgments of games from the times and places in which we encounter them. The beginning of my time with Heroes II corresponded with the height of the pandemic, when I didn’t have a whole lot else to do but write, play games, and go for long walks. Then I played it a lot more while I was working on my “Web Around the World” series, which left me with no big pressure to play other games for a good six months. I have fond memories of sitting on the terrace in weather fair and foul, talking with the neighbors from time to time over the hedge, and otherwise just happily playing away. Then my wife discovered that she liked the game a lot as well, and we started playing it together. All told, I’m sure that I put more hours into Heroes II than I have into any other game since I started this website.
Heroes III was not like that; it was just another game to have a look at, in a different, more distracted context. I still put quite some hours into it, more than I could strictly justify in the name of “research.” And almost all of those hours were once again spent in multi-player mode with my wife. We greatly appreciated the smoother networked play of Heroes III, as well as the abundance of cooperative multiplayer scenarios. (We much prefer to play that way rather than trying to kill one another.) But I didn’t feel the urge or the compulsion to play every scenario, as I had with Heroes II. There was a slight twinge of been-there, done-that for us both even when we were having fun.
All of which is to say that you shouldn’t take my word as gospel truth here, any more than you should for any game I write about. If I’d come to Heroes III first, and/or in a different time, I might very well be expressing a different opinion right now.
Even as it is, I cannot deny that Heroes of Might and Magic III is an immensely satisfying game in its own right, one which I feel no hesitation over inducting into my personal hall of fame. I still want to tell you that the best way to enjoy the series is to start at the beginning with the rather rudimentary but charming Heroes I — or perhaps even The King’s Bounty if you want to be really thorough about it — and make your way forward from there. But I do understand as well that life is short, time is limited, and not everyone is a digital antiquarian who can justify any portion of his playing time in the name of research. Heroes III is a perfectly fine place to jump in as well.
Released in February of 1999, Heroes of Might and Magic III was a solid early seller in its homeland, but not a massive, chart-busting one. It would prove more of a marathon runner than a sprinter. Aided by two expansion packs that added yet more campaigns, scenarios, monsters, treasures, and other goodies, along with one more faction to play and even a random map generator for those who had plowed through all of the set-piece content, it sold steadily for years on end, defying the conventional wisdom that turn-based, pixel-graphics games were a hopeless proposition in the marketplace. 3DO aided its cause greatly by investing in widespread language localization and making sure with the aid of various partners that Heroes III was readily available in shops all over the world.
It proved especially popular in Russia, where, unusually for a turn-based game, it even found a place in e-sports leagues. For decades now, people have been asking themselves just what is behind the special love that Heroes III sparked in the hearts of Russians. A possible answer might begin by noting that the traditional high-fantasy tropes that were always New World’s stock-in-trade seemed fresher in the lands that had been walled off behind the Iron Curtain than they did elsewhere, and might conclude by noting that Heroes III’s modest system requirements — no fancy 3D card required! — gave it a leg-up in countries where the average personal computer was not so powerful as in the richer West. Between these two data points lies a no man’s land of rank speculation. But for whatever combination of reasons, if you go to any online Heroes III scenario archive today, you’ll still find that a crazy percentage of the maps bear names written in Cyrillic. In a time of increasing global discord such as our own, it’s nice to be reminded that the sort of good, clean fun promised by Heroes remains universal.
I don’t believe that credible hard sales figures have ever emerged for any of New World’s games. But based on circumstantial evidence alone, I wouldn’t be at all surprised to learn that this one sold 2 million or even 3 million units before all was said and done. It most assuredly has to be the most successful single game New World ever made, as well as the most successful ever published by 3DO. (Granted, the latter is not a particularly high bar to clear…) When we consider the modest amount of money that was put into making Heroes III, we have a return on investment to die for, regardless of whether we calculate the bottom line in dollars and cents or hours of fun delivered.
Might and Magic VII: For Blood and Honor would prove less enduringly iconic than the third installment from its spinoff franchise, but it was a rock-solid effort in its own right. Bryan Farina and Paul Rattner, the principal designers of the previous game in the CRPG series, were joined this time by one James W. Dickinson. Might and Magic VII shipped in June of 1999, just thirteen months after Might and Magic VI and three months after Heroes III. On a schedule like that, there was no time for technological or philosophical reinvention — and, indeed, Might and Magic VII is even more of a strictly evolutionary step than Heroes III. It uses the same engine as its predecessor, with only a few minor tweaks here and there. Nevertheless, it’s a slightly better game than Might and Magic VI in my opinion, retaining most of the latter’s gonzo charm whilst feeling more manageable and self-consciously designed, as opposed to grown organically in some sort of nerdy laboratory of excess.
By now, it had become standard practice at New World to integrate the plots of the CRPGs and the strategy branches of the Might and Magic family tree. So, the story of Might and Magic VII follows on from that of the headline campaign of Heroes III, taking place on the same newly discovered continent of Erathia. Most of the old gang is back together again, including Queen Catherine, the star of Heroes III, and the dastardly Archibald, the villain you already defeated once in Heroes II. I’d tell you more about the story, but, honestly, if you’re playing a Might and Magic game for the plot, you’re doing it wrong.
That said, there are a few more nods here toward giving you some agency over the narrative beyond deciding where to go and kill monsters next; New World may have felt a sense of obligation to at least gesture in that direction after seeing the groundbreaking Interplay CRPGs Fallout and Baldur’s Gate. You’re forced to make a moral choice about whether to join the forces of light or darkness about one-half to two-thirds of the way through Might and Magic VII. Even so, a single hard branch like this is pretty weak sauce compared to the choices and consequences that are woven throughout a CRPG like Fallout. Might and Magic VII remains a fundamentally different type of game. And I for one wouldn’t have it any other way.
Where Might and Magic has always excelled is in giving you a giant, generous, unabashedly silly, blatantly artificial sandbox of a world to go forth and explore, exploit, and exterminate. The seventh game justifies its existence by giving you an even broader swath of fun stuff to do in the sandbox than its predecessor. You get a home base this time, a castle that you get to renovate step by step as you earn social credit from your adventures. Meanwhile the addition of an Invisibility spell opens up the possibility of sneaking your way through some areas instead of falling back on the standard approach of methodical monster genocide; Thief this game is not, but skulking about in a demon town whose inhabitants would reduce your party to a handful of smoking cinders in about half a second if they could only see them is not without its thrills.
Perhaps best of all — definitely so if you ask my wife — is a new card game called Arcomage, obviously inspired by Magic: The Gathering, that you can play in any and all of Erathia’s taverns; there’s even a quest that demands that you win a round of Arcomage in every single watering hole. I played Might and Magic VII on our living-room television, while my wife did her embroidery and mocked my ineptness and the game’s abject nerdiness — business as usual in our house over most of the seventeen years we’ve been married, in other words. But as soon as she saw Arcomage, she was smitten. I learned to avoid going into taverns unless I absolutely had to, because she would invariably demand the mouse in order to play a round or two or three. For this reason, I’ve never actually gotten the chance to play Arcomage myself, but it sure looks like good fun to me.
Certainly plenty of people have come to share my wife’s opinion of it over the years. In the immediate aftermath of Might and Magic VII‘s release, fans set up entire websites dedicated strictly to this game-within-a-game; the level of interest was so high that New World later published a standalone version of Arcomage, with networked multiplayer support. It would be going too far to say that Might and Magic VII is a mediocre CRPG that you have to tolerate in order to play an excellent card game, as people sometimes say of Final Fantasy VIII and its own built-in card game of Triple Triad. But Arcomage does add considerably to the already ample fun that awaits in Might and Magic VII. I know that it added quite some hours to my total play time in the CRPG, what with my wife’s addiction to it.
Other additions to the Might and Magic VI template are more commonsense than inspired, but nevertheless reflect a development team who were listening to the wishes and complaints of their players. It’s now possible to move your party after you’ve entered turn-based mode for combat, in just the same way that the monsters they’re fighting are allowed to move; names of important locations automatically appear on the auto-map; the auto-notes and quest log are little more thorough; the cheerfully janky graphics engine has become somewhat less so without losing its personality, with monsters being less likely now to get themselves stuck in walls and floors; a tutorial zone has been added for getting new players up to speed; etc, etc. Evolution rather than revolution, yes, but no less welcome for it.
The game is smaller than its predecessor — not small, but smaller — with more self-awareness of what it’s on about from moment to moment. The crazily ginormous dungeons of Might and Magic VI have become a bit more constrained, and each one here has a clear plot function, rather than existing just to exist. The sense that dogged Might and Magic VI that work on that game had not been so much completed as halted when the day to ship came is not present here; Might and Magic VII manages to feel like a fully realized, reasonably polished whole. All of these things make it the better game of the two by any objective measure, even if the monument to Monty Haul excess that is Might and Magic VI is in some cock-eyed way the more lovable creation. If you’re at all curious about the series today, the seventh game is probably the best place to start. If you still want more after you’re done with it, the lumpier pleasures of what came before — and after, for that matter — will still be there waiting for you.
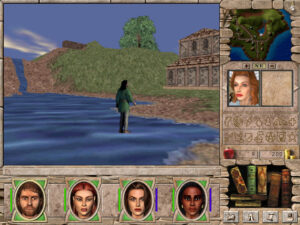
Walking on water. When I say this game is less janky than its predecessor, the “less” does a great deal of heavy lifting.
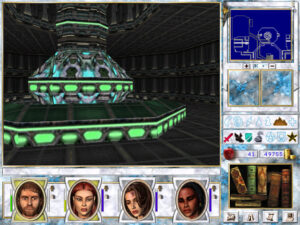
If you choose the path of light, you get to literally ascend to Heaven. (The opposite also applies.)
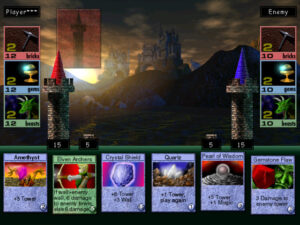
Here we go. Arcomage in all its pseudo-Magic: The Gathering glory. Do not, under any circumstances, let my wife see this screenshot, or I’ll be forced to boot up the game again.
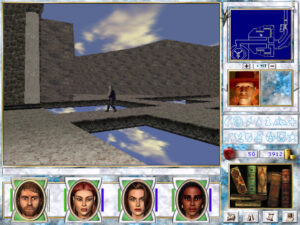
It wouldn’t be a Might and Magic CRPG if you didn’t wind up fighting robots in a dungeon that’s more George Lucas than J.R.R. Tolkien. By the seventh go-round, this was no longer quite the shock it once was, but series tradition must be served.
Magic and Magic VII was never expected to sell as well as Heroes III, and it delivered no surprises in this regard. In this era of rampant audiovisual one-upsmanship, many reviewers complained that it looked essentially the same as the previous game in the series, which had been no audiovisual wonder in itself. Enough gamers looked beyond the surface, however, to make it profitable. Again, firm New World sales figures are nonexistent, but 100,000 copies strikes me as a reasonable ballpark. Such a number was enough to ensure that New World would invest in a Might and Magic VIII, but not enough to encourage them to devote a great deal of resources to it. Indeed, as we’ll see in a later article, both Might and Magic and New World as a studio would become victims of the cruel logic of diminishing returns after this peak year of 1999.
Right now, though, we’ll leave New World on top of the world, or at least as close to it as they would ever get. For, as usual, we have much else to talk about before we can go from here to there.
Did you enjoy this article? If so, please think about pitching in to help me make many more like it. You can pledge any amount you like.
Sources: Computer Gaming World of July 1999, October 1999, and January 2000; Retro Gamer 49.
Those wishing for a more detailed chronicle of the development of Heroes III may want to look to the newsletter that Greg Fulton published in conjunction with a now-abandoned attempt to create a modern successor to the game. All of the standard caveats about single-source history apply — Fulton is not without axes to grind — but the spirit of the age, as they say, is there. For my part, I must admit that I’m most intrigued by Fulton’s ability to remember meals he ate a quarter-century ago, complete with cheesy fast-food branding. (“Following a quick run to the nearby Jack In The Box, for a Sourdough Jack and a couple Vile Tacos, I returned to my office.”) In addition to giving me a vicarious bellyache (“I gorged myself on a chili-cheese burger, two chili-cheese hot dogs, and a vanilla milkshake…”), this leaves me wondering why I can’t seem to remember what I ate for dinner last week. Anyway, Fulton starts to reminisce in earnest in the tenth issue of his newsletter, so that may be the best place to jump in.
Where to Get Them: Heroes of Might and Magic III: Complete and Might and Magic VII: For Blood and Honor are both available as digital purchases at GOG.com.