After Infocom was shut down in 1989, Mike Dornbrook, the mastermind behind the company’s InvisiClues hint books and much else that has become iconic for interactive-fiction fans of a certain generation, was determined to start a company of his own. Indeed, he was so motivated that he negotiated to take much of Infocom’s office furniture in lieu of cash as part of his severance package.
But alas, his entrepreneurial dream seemed vexed. He embarked on a mail-order catalog for maps and travel books — until he learned that Rand-McNally was starting a catalog of its own. He pivoted to offering customized traffic reports for drivers on the go — until it was decided by the authorities in the Boston area where he lived that mobile-phone users would not be allowed to call “premium-rate” numbers like the one he was setting up. So, in January of 1991, he started a regular job at a targeted-marketing and data-processing consultancy that had recently been purchased by American Express. Two years later, he was laid off, but carried his knowledge and contacts into his own data-mining startup. He was still trying to line up enough investment capital to get that company going properly when he got a call from Steve Meretzky, who before becoming a star Infocom designer had been his roommate in a little Boston apartment; in fact, it was Dornbrook who had first introduced Meretzky to the wonders of Zork, thus unleashing him on the world of adventure games.
Unlike Dornbrook, Meretzky had stayed in the games industry since Infocom’s shuttering, designing four adventures for Legend Entertainment and one for Activision from his Boston home. But he had grown tired of working remotely, and dearly missed the camaraderie and creative ferment of life at Infocom. Superhero League of Hoboken, his latest game for Legend (and by far the most inspired of his post-Infocom career in this critic’s opinion), had turned into a particularly frustrating experience for him; delays on the implementation side meant that it was still many months away from seeing the light of day. He had thus decided to start a games studio of his own — and he wanted his old pal Mike Dornbrook to run it for him. “I’ll help you to get it going,” agreed a somewhat reluctant Dornbrook, who after enduring the painful latter years of Infocom wasn’t at all sure he actually wanted to return to the industry.
And so Boffo Games was born. Sadly, all of Dornbrook’s forebodings would prove prescient.
At the time, the hype around multimedia computing was reaching a fever pitch. One of the biggest winners of the era was a Singaporean company called Creative Labs, whose Sound Blaster sound cards had been at the vanguard of a metamorphosis in computer audio since 1989. More recently, they had also begun selling CD-ROM drives, as well as “multimedia upgrade kits”: sound cards and CD-ROM drives in one convenient package, along with a few discs to get purchasers started on their magical journey.
Of late, however, another company had begun making waves in the same market. The Silicon Valley firm Media Vision had first captured headlines in newspaper financial sections in November of 1992, when it raised $45 million in an initial public offering in order to go head to head with Creative. Soon after, Media Vision released their Pro AudioSpectrum 16 sound card, the first to offer 16-bit — i.e., audio-CD-quality — sound playback. It took Creative months to follow suit with the Sound Blaster 16.
But Media Vision’s ambitions extended well beyond the sound-card and CD-ROM-drive market, which, as most financial analysts well realized, looked likely to plateau and then slowly tail off once everyone who wanted to add multimedia capabilities to an existing computer had done so and new computers were all shipping with these features built-in. To secure their long-term future, Media Vision planned to use their hardware profits to invest heavily in software. By the Christmas buying season of 1993, announced the company’s CEO Paul Jain at the beginning of that same year, they would have ten cutting-edge CD-ROM games on the market. To prove his bona fides, he had recruited to run his games division one Stan Cornyn, a legendary name among music-industry insiders.
Cornyn had been hired by Warner Bros. Records in 1958 to write liner notes, and had gone on to become instrumental in building Warner Music into the biggest record company in the world by the end of the 1980s, with superstars like Madonna and Prince in its stable of artists. During his last years at Warner, Cornyn had headed the Warner New Media spinoff, working on Philips CD-I titles and such other innovations as the CD+G format, which allowed one to place lyrics sheets and pictures on what were otherwise audio CDs. In 1992, he had left Warner. “Corporate [leadership] wanted my company to turn a profit, and I had no idea how our inventions would conquer the world,” he would write later. “That, I left to others.” Instead he decided to reinvent himself as a games-industry executive by signing on with Media Vision. His entrance said much about where the movers and shakers in media believed interactive entertainment was heading. And sure enough, he almost immediately scored a major coup, when he signed press darling Trilobyte to release their much-anticipated sequel to The 7th Guest under the Media Vision banner.
As it happened, Marc Blank, one of the original founders of Infocom, had worked at Warner New Media for a time with Cornyn; he had also remained friendly with both Mike Dornbrook and Steve Meretzky. When he read about Cornyn’s hiring by Media Vision, it all struck Dornbrook as serendipitous. “I thought, ‘Aha!'” he remembers. “‘We have a new person who needs content and has a massive budget, and we have a connection to him.'” It was now the fall of 1993. Media Vision hadn’t published the ten games that Paul Jain had promised by this point — they’d only managed two, neither of them very well-received — but that only made Cornyn that much more eager to sign development deals.
Blank proved as good a go-between as Dornbrook had hoped, and a meeting was arranged for Monday, January 17, 1994, in the Los Angeles offices of Stan Cornyn’s operation. Taking advantage of cheaper weekend airfares, Dornbrook and Meretzky took off from a Boston winter and landed amidst the storied sunshine of Southern California two days before that date. Looking at the pedestrians strolling around in their shorts and flip-flops while he sweated in his winter pullover, Dornbrook said to his friend, “You know, I can kind of see why people want to live out here.”
“You’d never catch me out here,” answered Meretzky, “because of the earthquakes.”
“It would be just our luck, wouldn’t it…” mused Dornbrook.
Fast-forward to 4:30 AM on Monday morning, in the fourth-floor hotel room they were sharing. Dornbrook:
The initial shock threw Steve out of his bed and threw me up in the air. I grabbed onto my mattress and held on for dear life. It was like riding a bucking bronco. The building was shaking and moving in ways I didn’t think a building could survive. I was convinced that at any second the ceiling beams were going to fall on me and crush me. That went on for 35 seconds — which feels like about five minutes in an earthquake. And then it stopped.
We were both fine, but it was pitch black in the room; all the lights were out. But I noticed there was a little red light on the TV. I thought, “Oh, we still have power.” So, I decided to turn the TV on. All my life, the public-broadcast system was telling me, in case of an emergency, they would tell me what to do. While I’m turning it on, Steve is yelling, “We need to get out of here!”
I said, “I want to see what they’re telling us to do.” It was a newsroom in LA, one of the main network stations. The camera was zoomed all the way back in a way you normally didn’t see. There were all these desks, all empty except one. That person was screaming and putting his hands over his head and crawling under the desk — and then the power went out.
I knew the TV station was many, many miles from us. This was not just local; this was a major quake. I’m thinking that the San Andreas Fault might have given way. We might not have water; we’re in a desert. We might be trapped here with no water! So, I crawled into the bathroom and started filling the bathtub with water. Steve is yelling, “What the hell are you doing? We’ve got to get out of here!”
I said, “We need water!”
After the bathtub was full, we got dressed in the dark and worked our way down the hall. We had no way of knowing if there was floor in front of us; it was pitch black. So, I let him go first. He felt his way down the hall, making sure there was a floor there. We got to the exit stairs, and they were pitch black also. We went down step by step, making sure there was another step in front of us, all the way to the first floor.
Then we opened the door into the parking lot, and I remember gasping at the sight. We’re in a desert, it’s dry as can be, and there’s no power for hundreds of miles. You could see stars right down to the horizon. I’ve never seen a sky so clear. It was stunning.
The 1994 Los Angeles earthquake killed 57 people, injured more than 9000, and did tens of billions of dollars of property damage. But the show must go on, as they say in Hollywood. The meeting with the Media Vision games division convened that afternoon in Stan Cornyn’s house, delayed only about six hours by the most violent earthquake in Los Angeles history.
Anyone familiar with my earlier coverage of Steve Meretzky’s career will know that he collected game ideas like some people collect stamps. True to form, he showed up at Cornyn’s house with no less than 21 of them, much to the chagrin of Dornbrook, who would have vastly preferred to pitch just one or two: “Because they don’t really have a clue what will work, and they think you do.” On this occasion, though, everyone in the room was feeling giddy from having survived the morning, not to mention the bottles of good wine Cornyn brought up from his cellar, as they listened to Meretzky work through his list. When he was finally finished, Cornyn and his team huddled together for a few minutes, then returned and announced that they’d take eleven of them, thank you very much, and they’d like the first by Christmas at the latest. As a demonstration of good faith while the lawyers wrote up the final contracts, Cornyn handed Dornbrook and Meretzky a check for $20,000. “Get started right now,” he said. “We don’t want you to lose a day.”
After they’d digested this bombshell, Dornbrook and Meretzky asked each other which idea they could possibly bring to fruition in the span of just nine months or so, given that they were literally starting from scratch: no office, no staff, no computers, no development tools, no investors. (Boffo’s founding capital had been exactly $10.) They decided on something called Hodj ‘n’ Podj.
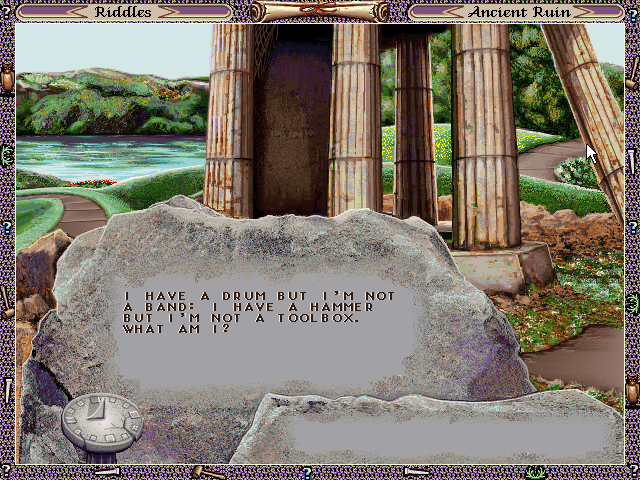
Hodj ‘n’ Podj wasn’t a traditional adventure game, but it was a classic Steve Meretzky project, a game concept which had caught his fancy a long time ago and had remained in his notebook ever since. Its origins reached back to Fooblitzky, the most atypical Infocom game ever: a multiplayer board game that happened to be played on the computer, designed mostly by Mike Berlyn circa 1984. It was a roll-and-move game which revolved around deducing which four of eighteen possible items your character needed to collect in order to win, and then carrying them across the finish line before your competitors did the same with their collections. Played on the company’s big DEC PDP-10, Fooblitzky was a fixture of life inside mid-period Infocom. In late 1985, it became the one and only Infocom product to use their little-remembered cross-platform graphics engine, becoming in the process something of a case study in why such an engine was more problematic than their ubiquitous textual Z-Machine: Fooblitzky shipped only for the IBM PC, the Apple II, and the Atari 8-bit line of computers, running on the last two at the speed of treacle on a cold day and not coming close to utilizing the full graphics capabilities, modest though they may have been, of any of its hosts. A casual family game at a time when such things were virtually unheard of on computers, and a completely silent and graphically underwhelming one at that, it sold only about 7500 copies in all.
Meretzky’s idea, then, was to update Fooblitzky for an era of home computing that ought to be more friendly to it. He would retain the core mechanics — roll and move, deduce and fetch — but would polish up the interface and graphics, write a fresh framing story involving a kidnapped princess in a fairy-tale kingdom, and add one important new element: as you moved around the board, you would have to play puzzle- and/or action-based mini-games to earn the clues, items, and money you needed. The game would run under Windows — no futzing about with MS-DOS IRQ settings and memory managers! — in order to reach beyond the hardcore-gamer demographic who would probably just scoff at it anyway. It seemed a more than solid proposition, with an important practical advantage that shot it right to the top of Boffo’s project list: the mini-games, where the bulk of the programming would be required, were siloed off from one another in such a way that they could be developed by separate teams working in parallel. Thus the project should be finishable in the requested nine months or so.
Back in cold but blessedly stable Boston, Dornbrook and Meretzky rented office space, hired staff, and bought computers on Media Vision’s dime. The final contract arrived, and all still seemed fine, so much so that Dornbrook agreed to wind up his data-mining venture in favor of doing games full time again. Then, one morning in early April, he opened his newspaper to read that Media Vision was being investigated by the Securities and Exchange Commission for serious accounting malfeasance.
In retrospect, the signs had been there all along, as they usually are. The move into software should have raised antennas already more than a year before. “When a company switches or expands its business line into something completely different, it generally means management fears that growth will slow in the main line,” wrote stock-market guru Kathryn F. Staley as part of the round of Monday-morning quarterbacking that now began. “When they expand into a highly competitive business that costs money for product development (like software game titles) when the base business eats money as well, you sit back and watch for the train wreck to happen.” Herb Greenberg, a financial correspondent for the San Francisco Chronicle, had been sounding the alarm about Media Vision since the summer of 1993, noting how hard it was to understand how the company’s bottom line could look as good as it did; for all the buzz around Media Vision, it was Creative Labs who still appeared to be selling the vast majority of sound cards and CD-ROM drives. But nobody wanted to listen — least of all two Boston entrepreneurs with a dream of starting a games studio that would bring back some of the old Infocom magic. Media Vision’s stock price had stood at $46 on the day of that earthquake-addled meeting in Los Angeles. Four months later, it stood at $5. Two months after that, the company no longer existed.
As the layers were peeled away, it was learned that Paul Jain and his cronies had engaged in a breathtaking range of fraudulent practices to keep the stock price climbing. They’d paid a fly-by-night firm in India to claim to have purchased $6 million worth of hardware from them that they had never actually made. They’d stashed inventory they said they had sold in secret warehouses in several states. (This house of cards started to fall when Media Vision’s facilities manager, who was not in on the scheme, asked why she kept getting bills from warehouses she hadn’t known existed.) They’d capitalized the expense of their software projects so as to spread the bills out over many years — a practice that was supposed to be used only for permanent, ultra-expensive infrastructure like factories and skyscrapers. Herb Greenberg revealed in one of his articles that they’d go so far as to capitalize their corporate Christmas party. After long rounds of government investigations and shareholder lawsuits, Paul Jain and his chief financial officer Steve Allan would be convicted of wire fraud and sentenced to prison in 2000 and 2002 respectively. “This was certainly one of the dirtiest cases I was ever involved in,” said one lawyer afterward. There is no evidence to suggest that Stan Cornyn’s group was aware of any of this, but the revelations nevertheless marked the end of it alongside the rest of Media Vision. Cornyn himself left the games industry, never to return — understandably enough, given the nature of his brief experience there.
Showing amazing fortitude, Dornbrook, Meretzky, and the team of programmers and artists they’d hired just kept their heads down and kept working on Hodj ‘n’ Podj while Media Vision imploded. When the checks stopped coming from their benefactor, the founders quit paying themselves and cut all other expenses to the bone. That October, Hodj ‘n’ Podj was finished on time and under budget, but it was left in limbo while the bankruptcy court sorted through the wreckage of Media Vision. In December, the contract was bought at the bankruptcy fire sale by Virgin Interactive, and against all odds the game reached store shelves under their imprint in March of 1995. (Virgin also wound up with The 11th Hour, the sequel to The 7th Guest — an ironic and rather delicious turn of events for them, given that they had actually been the publisher of The 7th Guest back in the day, only to be abandoned by a starstruck Trilobyte when the time came to make the sequel.)
Hard sales figures for Hodj ‘n’ Podj aren’t available, but we can say with confidence that it wasn’t a big seller. In a 1998 Game Developers Conference presentation, Dornbrook blamed a shakeup at Virgin for its disappointing performance. It seems that the management team that bought it at the bankruptcy sale was excited about it, but another team that replaced the first was less so, and this latter refused to fund any real advertising.
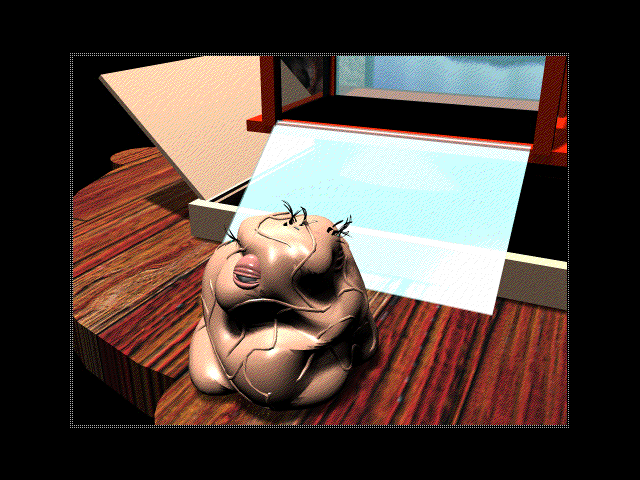
These things were doubtless a major factor in its lack of commercial success, but it would be a bridge too far to call Hodj ‘n’ Podj a neglected classic. Although it’s bug-free and crisply presented, it wears out its welcome way more quickly than it ought to. A big part of the problem is the mini-games, which are one and all reskinned rehashes of hoary old perennials from both the analog and digital realms: Battleship, cryptograms, Solitaire, Kalah, video poker, etc. (“These tired old things are games you could play in your sleep, and a bit of freshening up on the soundtrack does little to encourage you to stay awake,” wrote Charles Ardai, harshly but by no means entirely inaccurately, in his review for Computer Gaming World.) Hodj ‘n’ Podj gives you no reason to explore the entire board, but rather makes the most efficient winning gambit that of simply hanging around the same few areas, playing the mini-games you are best at over and over; this speaks to a game that needed a lot more play-testing to devise ways to force players out of their comfort zones. But its most devastating weakness is the decision to support only two players in a game that positively begs to become a full-blown social occasion; even Fooblitzky allows up to four players. A board filled with half a dozen players, all bumping into and disrupting one another in all kinds of mischievous ways, would make up for a multitude of other sins, but this experience just isn’t possible. Hodj ‘n’ Podj isn’t a terrible game — you and a friend can have a perfectly enjoyable evening with it once or twice per year — but its concept is better than its implementation. Rather than becoming more interesting as you learn its ins and outs, as the best games do — yes, even the “casual” ones — it becomes less so.
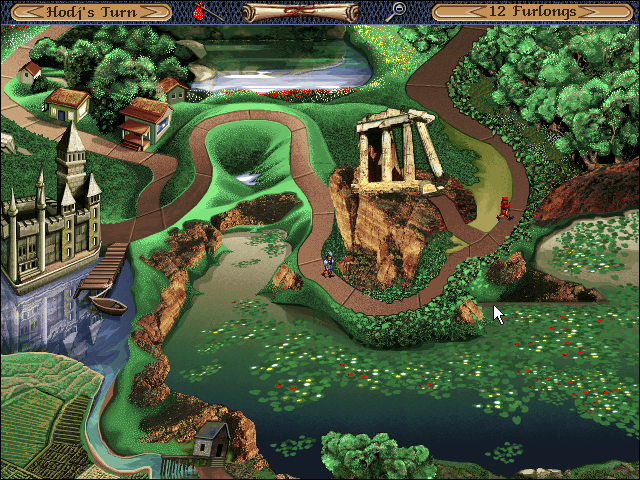
The main game board. Whatever else you can say about it, Hodj ‘n’ Podj is beautifully presented, thoroughly belying its hurried assembling by a bunch of short-term hired hands. Its pixel art still looks great today.
After Hodj ‘n’ Podj, the story of Boffo turns into a numbing parade of games that almost were. By Mike Dornbrook’s final tally, 35 of their proposals were met with a high degree of “interest” by some publisher or another; 21 led to “solid commitments”; 17 garnered verbal “promises”; 8 received letters of intent and down payments; 5 led to signed contracts; and 2 games (one of them Hodj ‘n’ Podj) actually shipped. I don’t have the heart to chronicle this cavalcade of disappointment in too much detail. Suffice to say that Boffo chose to deal — or was forced to deal — mostly with the new entities who had entered the market in the wake of CD-ROM rather than the old guard who had built the games industry over the course of the 1980s. As the venture capitalists and titans of traditional media who funded these experiments got nervous about a multimedia revolution that wasn’t materializing on the timetable they had expected, they bailed one by one, leaving Boffo out in the cold. Meanwhile the hardcore gaming market was shifting more and more toward first-person shooters and real-time strategy, at the expense of the adventure games which Steve Meretzky had always created. The most profitable Boffo project ever, notes Dornbrook wryly, was one which disappeared along with Time Warner Interactive, leaving behind only a contract which stipulated that Boffo must be paid for several months of work that they now didn’t need to do.
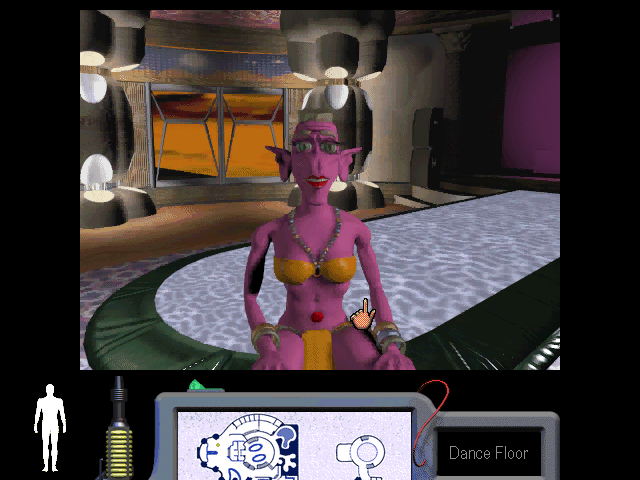
But Boffo did manage to complete one more game and see it released, and it’s to that project that we’ll turn now. The horrid pun that is its title aside, the thunderingly obvious inspiration for Steve Meretzky’s The Space Bar is the cantina scene from Star Wars, with its dizzying variety of cute, ugly, and just plain bizarre alien races all gathered into one seedy Tatooine bar, boozing, brawling, and grooving to the music. Meretzky wanted to capture the same atmosphere in his game, which would cast its player as a telepathic detective on the trail of a shapeshifting assassin. To solve the case, the player would not only need to interrogate the dozens of aliens hanging out at The Thirsty Tentacle, but enter the minds of some of them to relive their memories. Meretzky:
The main design goal for the project was to create an adventure game which was composed of a lot of smaller adventure games: a novel is to a short-story collection as a conventional adventure game would be to The Space Bar. In addition to just a desire to try something different, I also felt that people had increasingly scarce amounts of [free] time, and that starting an adventure game required setting aside such a huge amount of time, many tens of hours. But if, instead, you could say to yourself, “I’ll just play this ‘chapter’ now and save the rest for later,” it would be easier to justify picking up and starting the game. Secondary design goals were to create a spaceport bar as compelling as the one in the first Star Wars movie, to create a Bogart-esque noir atmosphere, to be really funny, and to prove that you could make a graphic adventure that, like the Infocom text games, could have a lot of “meat on the bones.” As with Hodj ‘n’ Podj, I felt that just a collection of independent games was too loose and required a connecting thread; thus the meta-story involving [the player character] Alien Node’s search for the shapeshifter Ni’Dopal. Empathy Telepathy was just a convenient device for connecting the “short stories” to the meta-story.
In the spring of 1995, the tireless Mike Dornbrook was on the verge of clinching a deal to make this game — and for once it was not a deal with a trend-chasing multimedia dilettante: he had no less enviable a fish than Microsoft on the hook. Then Meretzky learned of a startup called Rocket Science Games that had on its staff one Ron Cobb, a visual-design legend who had crafted the look of such films as Alien, The Terminator, Back to the Future (yes, the Delorean time machine was his…), The Abyss, and Total Recall, who had even according to Hollywood rumor been the uncredited creator of E.T., Steven Spielberg’s $792 million-grossing extra-terrestrial. But before all of that, Cobb had made his name by doing the cantina scene for Star Wars. It would be crazy to pass up the chance to have him create the aliens in The Space Bar, said Meretzky. Dornbrook thought it was far crazier to turn down a deal with Microsoft in favor of an unproven startup, but he sighed and made the calls. Soon after, Boffo signed a contract with Rocket Science.
Once again, the warning signs were all there, at least in retrospect. Rocket Science’s founder Steve Blank (no relation to Marc Blank) was a fast-talking showman fond of broad comparisons. His company was “Industrial Light & Magic and Disney combined!” he said. Or, even more inexplicably, it was Cream, the 1960s rock supergroup. Tellingly, none of his comparisons betrayed any familiarity with the current games industry. “Rocket Science feels good and looks good, even though when someone asks me to describe it, I’m somewhat at a loss,” said Blank. In most times and places, a founder unable to describe his company is cause for concern among pundits and investors. But in Silicon Valley in 1995, it was no problem as long as its products were to ship on little silver discs. Blank told his interviewers that he was so awash in investment capital that he could run his company for five years without pulling in any revenue at all.
That was the version of Rocket Science which Boffo signed on with, the one which was capturing the cover of Wired magazine. The following year, “I found out that our games are terrible, no one is buying them, our best engineers [have] started leaving, and with 120 people and a huge burn rate, we’re running out of money and about to crash,” Blank later remembered in a mea culpa published in Forbes. The games in question consisted mostly of simplistic arcade-style exercises, not terribly well designed or implemented, threaded between filmed video snippets, not terribly well written or acted. Gamers took one look at them and then returned to their regularly scheduled sessions of DOOM and Warcraft.
Just as they had with Hodj ‘n’ Podj, Boffo kept their heads down and kept working on The Space Bar while Rocket Science was “cratering,” to use Steve Blank’s favorite vernacular. Meretzky did get to work with Ron Cobb on the visual design, which was quite a thrill for him. A seasoned animation team under Bill Davis, Sierra On-Line’s former head of game visuals, created the graphics using a mixture of pixel art and 3D models, with impressive results. Everyone kept the faith, determined to believe that a game as awesome as this one was shaping up to be couldn’t possibly fail — never mind the weakness of Rocket Science, much less the decline of the adventure-game market. As the months went by and the reality of the latter became undeniable, Meretzky and his colleagues started to talk about The Space Bar as the game that would bring adventures back to the forefront of the industry. “We concentrated on making The Space Bar such a winner that everyone would want to work with us going forward,” says Dornbrook.
In the meantime, Rocket Science continued its cratering. The embattled Steve Blank was replaced by Bill Davis in the CEO’s chair in 1996, and this bought the company a bit more money and time from their investors. In the long run, though, this promotion of an animation specialist only emphasized Rocket Science’s core problem: a surfeit of audiovisual genius, combined with a stark lack of people who knew what made a playable game. In April of 1997, the investors pulled the plug. “It’s tragic when a collection of talent like Rocket Science assembled is disbanded,” said Davis. “It’s a great loss to the industry.” Yet said industry failed to mourn. In fact, it barely noticed.
The Space Bar was in its final stages of development when the news came. Boffo’s contract was passed to SegaSoft, the software division of videogame-console maker Sega, who had invested heavily in Rocket Science games for the underwhelming Sega Saturn. Dornbrook and Meretzky couldn’t help but feel a sense of déjà vu. Just as had happened with Hodj ‘n’ Podj, The Space Bar was crawling out from under the wreckage of one publisher into the arms of another who didn’t seem to know quite what to do with it. In the weeks before the game’s release, SegaSoft ran a series of weirdly tone-deaf advertisements for it; for reasons that no one could divine, they were take-offs on the tabloid journalism of The National Enquirer. They were so divorced from the game they claimed to be promoting that the one silver lining, says Dornbrook, was that “at least no one would associate them with our game.”
Unlike Hodj ‘n’ Podj, The Space Bar didn’t prove a commercial disappointment: it turned into an outright bomb. Meretzky still calls its disastrous failure the bitterest single disappointment of his career. Soon after, he and Dornbrook finally gave up and shuttered Boffo. Four years of failure and frustration were enough for anyone.
Dornbrook’s 1998 GDC presentation on the rise and fall of Boffo focused almost exclusively on the little studio’s poor treatment by its larger partners, on the many broken promises and breaches of faith they were forced to endure, until they could endure no more. But at the end of it, he did acknowledge that he might appear to be “blaming all of this on others. Weren’t we also at fault here? Did we have problems on our end?” He concluded that, an unfortunate decision here or there aside — the decision to sign with Rocket Science instead of Microsoft certainly springs to mind — they largely did not. He noted that they never failed to emphasize their biggest strength: “Steve’s a fantastic game designer.”
Does The Space Bar support this contention?
On the surface, the game has much going for it: its rogues’ gallery of misfit aliens is as ingenious and entertaining as you would expect from a meeting of the minds of Steve Meretzky and Ron Cobb; it’s as big and meaty as advertised, packed wall to wall with puzzles; its graphics and voice acting are mostly pretty great; it fills three CDs, and feels like it ought to fill even more. It’s the product of a team that was obviously thinking hard about the limitations of current adventure games and how to move past them — how to make the genre more welcoming to newcomers, as well as tempting once again for those who had gotten tired of the adventure-game status quo and moved on to other things. Among its innovative interface constructs are an auto-map that works wonderfully and a comprehensive logbook that keeps track of suspects, clues, and open puzzles. Dornbrook has called it “a labor of love,” and we have no reason to doubt him.
Nevertheless, it is — and it gives me no pleasure to write this — a flabbergastingly awful game. It plays as if all those intense design discussions Meretzky took part in at Infocom never happened, as if he was not just designing his first adventure game, but was the first person ever to design an adventure game. All the things that Ron Gilbert told the world made adventure games suck almost a decade earlier are here in spades: cul-de-sacs everywhere that can only be escaped by pressing the “restore” button, a need to do things in a certain order when you have no way of knowing what that order is, a need to run though the same boring processes over and over again, a stringent time limit that’s impossible to meet without hyper-optimized play, player deaths that come out of nowhere, puzzles that make sense only in the designer’s head. It’s not just sadistically but incompetently put together as a game. And as a marketplace proposition, it’s utterly incoherent, not to say schizophrenic; how can we possibly square this design with Meretzky’s stated goal of making a more approachable adventure game, one that would be digestible in snack-sized chunks? The Space Bar would seem to be aimed at two completely separate audiences, each the polar opposite of the other; I don’t believe there’s any hidden demographic of casual masochists out there. And there’s no difficulty slider or anything else that serves to bridge the chasm.

One of the oddities of the Boffo story is the sanguine belief on the part of the otherwise savvy Mike Dornbrook that he could use Steve Meretzky’s supposed “star power” to sell games, as demonstrated by his prominent billing here on the cover of the Space Bar box. Meretzky wasn’t any Sid Meier or John Romero; he was a cult figure rather than a household name even among hardcore gamers, adored by a small group of them for his work with Infocom but largely unknown to the rest of them. His last game to sell over 100,000 copies had been Leather Goddesses of Phobos in 1986, his last to manage 50,000 Spellcasting 101 in 1990.

These aliens are among the funniest. They’re an incredibly advanced and powerful race, but they look like Tiki drinks, and everyone is forever picking them up and trying to sip from them.
If The Space Bar sold ten copies, that was ten too many; I hope those ten buyers returned it for a refund. I don’t blame Mike Dornbrook for not being aware of just how terrible a game The Space Bar was; he was way too close to it to be expected to have an objective view under any circumstances, even as he was, as he forthrightly acknowledges, never really much of a gamer after his torrid early romance with Zork had faded into a comfortable conviviality. Still, to analyze the failure of Boffo only in terms of market pressures, bad luck, and perhaps just a few bad business choices is to fail at the task. In addition to all of these other factors, there remains the reality that neither of their two games were actually all that good. Nothing about The Space Bar would lead one to believe that Steve Meretzky is “a fantastic game designer.”
Yet Meretzky could in fact be a fantastic game designer. Back in 2015, writing about his 1987 Infocom game Stationfall, I called him “second to no one on the planet in his ability to craft entertaining and fair puzzles, to weave them together into a seamless whole, and to describe it all concisely and understandably.” I continue to stand by that statement in the context of his games of that era. So, how did we get from Stationfall to The Space Bar?
I belabor this question not because I want to pick on Steve Meretzky, whose half-dozen or so stone-cold classic games are half a dozen more than I can lay claim to, but because I think there’s an important lesson here about the need for collaboration in game design. I tend to see Meretzky’s rather disappointing output during the 1990s — including not only his Boffo games but those he did for Legend and Activision — as another ironic testament to Infocom’s genius for process. Infocom surrounded the designer of each of their games with skeptical, questioning peers, and expected him to work actively with a team of in-house testers who were empowered to do more than just point out bugs and typos, who were allowed to dig into what was fun and unfun, fair and unfair. Meretzky never worked in such an environment again after Infocom — never worked with people who were willing and able to tell him, “Maybe this joke goes on a bit too long, Steve,” or, “Maybe you don’t need to ask the player to go through this dozen-step process multiple times. ” The end results perhaps speak for themselves. Sometimes you need colleagues who do more than tell you how fantastic you are.
Steve Meretzky never designed another full-fledged adventure game after The Space Bar. Following a few dissatisfying intermediate steps, he found his way into the burgeoning world of casual social games, distributed digitally rather than as boxed products, where he’s done very well for himself since the turn of the millennium. Meanwhile Mike Dornbrook signed on with a little company called Harmonix that reminded him somewhat of Infocom, being staffed as they were with youthful bright sparks from MIT. After years of refining their techniques for making music interactive for non-musicians, they released something called Guitar Hero in 2005. Both of the principals behind Boffo have enjoyed second acts in the games industry that dwarf their first in terms of number of players reached and number of dollars earned. So, it all worked out okay for them in the end.
(Sources: the books Games Design Theory and Practice, second edition, by Richard Rouse III Exploding: The Hits, Hype, Heroes, and Hustlers of the Warner Music Group by Stan Cornyn, Capital Instincts: Life as an Entrepreneur, Financier, and Athlete by Richard L. Brandt, Thomas Weisel, and Lance Armstrong, and The Art of Short Selling by Kathryn F. Staley; Computer Gaming World of May 1995, August 1995, May 1997, and December 1997; Questbusters 116; Computer Games Strategy Plus of August 1996; Wired of November 1994 and July 1997; San Francisco Chronicle of August 29 2000; the June 1993 issue of Sierra’s customer newsletter InterAction. Online source include a CD Mag interview with Steve Meretzky, an Adventure Classic Gaming interview with Steve Meretzky, a Happy Puppy interview with Steve Meretzky, “Failure and Redemption” by Steve Blank at Forbes, and Mike Dornbrook’s presentation “Look Before You Leap” at the 1998 Game Developers Conference. But my most valuable source of all was Karl Kuras’s more than four-hour (!) interview with Mike Dornbrook for his Video Game Newsroom Time Machine podcast, a truly valuable oral history of the games industry from a unique perspective. Thanks, Karl and Mike!)