Mystery stories have been a staple of adventure gaming since 1978’s Mystery Mansion. That’s little surprise; no other form of traditional static literature so obviously sees itself as a form of game between reader and writer, and thus is so obviously amenable to adaptation into other ludic forms. Said adaptations existed well before the computer age, in such forms as the Baffle Books of the 1920s, the Dennis Wheatley Crime Dossiers of the 1930s, and the perennial board game Cluedo (Clue in North America) of 1949.
The early computerized mystery games had the superficial trappings of classic mystery literature but little of the substance. Games like Mystery Mansion and Mystery House were essentially standard Adventure-style treasure hunts, full of mazes and static puzzles, that happened to play out on the stage set of a mystery story. It really wasn’t possible to implement much else with, say, On-Line’s primitive Hi-Res Adventure engine.
That, of course, is why Infocom’s Deadline came as such a revelation. Unlike virtually everyone else making adventure games as of 1982, Infocom had the tools to do a mystery right, to capture the spirit and substance of classic mystery stories in addition to the window dressing. With such a proof of concept to examine (and one which proved to be a major hit at that), combined with a recent uptick in interest in the mystery genre within ludic culture in general following the republication of the old Dennis Wheatley dossiers and an elaborate new board game called Sherlock Holmes: Consulting Detective, other developers started diving into mysteries with similar earnestness. Some of them worked in the text-adventure form, but others branched out into other paradigms. For instance, Spinnaker’s two child-oriented Snooper Troops games and CBS Software’s two adult-oriented Mystery Master games replaced parsers and a single complex story with a more casual form of crime solving. Each contains a series of shorter cases to solve by traveling around a graphical city map, ferreting out clues at each location using a menu-driven interface. A top rating is achieved by solving the crime quickly, using a minimum of clues.
And then there was the game that would become known mostly as that other Free Fall game after the huge success of Archon: Murder on the Zinderneuf. It’s that most interesting anomaly that pops up more than you might expect, an adventure game designed by someone who didn’t much like adventure games.
Jon Freeman laid out his objections to traditional adventure games in an article in the December 1980 issue of Byte, contrasting the form and its limitations with those of the CRPG form he was then working with in crafting Automated Simulations’s DunjonQuest games. An adventure game, he says, is so static that it’s hardly a game at all. It’s “really a puzzle that, once solved, is without further interest.” The former part of this claim became increasingly less true as more dynamic, responsive game worlds like that of Deadline were developed, but the latter part… well, it’s hard to deny that point. The real question is to what extent this bothers you. One remedy to this fundamental failing is perhaps to create longer, deeper works that take as long to play once as it might take you to exhaust the interest of another type of game over many, many plays. Another, of course, is to simply say so what, to note that no one ever criticizes other forms of art, like books, for not being infinitely re-readable (not that Shakespeare doesn’t come close). But still, a re-playable adventure (or for that matter re-readable book) would, all else being held equal, be superior to a non-re-playable version of the same game. Freeman, who still lists Cluedo amongst his favorite games of all time, recycled that game’s concept on the computer, but fleshed out the suspects, the setting, the randomly generated stories behind the murders themselves, to make something more in line with the expectations of adventure gamers.
The mystery may change, but the setting and the actors, the raw materials of these little computer-generated dramas, must inevitably remain the same. Luckily, they’re pretty inspired. The game takes place in 1936, the heyday of the rigid airship, surely one of the most romantic and just plain cool methods of travel ever invented. On a trans-Atlantic voyage aboard the fictional German airship Zinderneuf, a murder has been committed. Which of the sixteen passengers was killed, and which did the killing, and why… these are the elements that are generated anew each time. As a whole genre of pulp-action tabletop RPGs have taught us, the 1930s are a wonderful period for fans of intrigue and derring-do, and Zinderneuf uses that well. Freeman and Reiche work in a lot of the era’s touchstones: old Hollywood, action serials, the Berlin Olympics, the Spanish Civil War, the mob, Amelia Earhart, spiritualism, adventurous archaeologists (Raiders of the Lost Ark was still huge while they worked on the game), and of course Communists and Nazis. It’s an effervescent, pulpy version of history. (That said, our libertarian friend Freeman just can’t restrain himself from taking a political shot at Franklin Delano Roosevelt that strikes a weird sourpuss note amongst all the fun: “Roosevelt was still offering his own version of ‘bread and circuses’ as he ‘guided’ the United States through an unprecedented four terms of depression and war.”) The Zinderneuf itself, meanwhile, proves perfect for a Murder on the Orient Express-style whodunnit. Playing as one of eight detectives drawn from literature or television — including homages to Mike Hammer, Miss Marple, Columbo, and the inevitable Sherlock Holmes among others — you have twelve hours to solve the case before the Zinderneuf touches down in New York and the suspects all scatter to the winds.
Those twelve hours translate to just 36 minutes of game time — yes, this is a real-time game. The idea here was to replace a 40-hour adventure game with a half-hour game that “can be replayed 100 times.” Also replaced are the text and parser, with a top-down graphical display and an entirely joystick-driven interface.
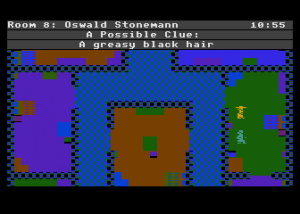
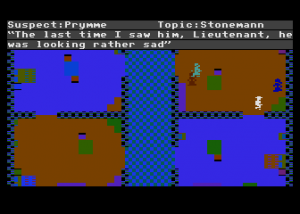
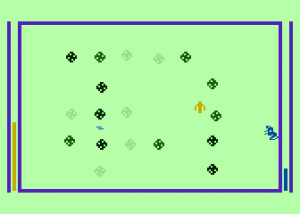
Each game begins by telling you who has been murdered from among the cast of characters, each of whom receives a capsule bio in the manual. And then, as Holmes would say (and the manual happily quotes), the game is afoot. You collect evidence in two ways. First, you can search the cabins of the victim and any of the other passengers to see what connections you can discover.
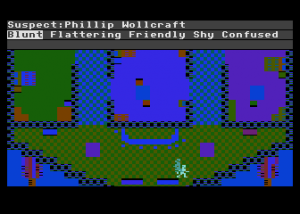
In the case above, I now know that the murderer of Oswald Stonemann is most likely someone with black hair; the victim is always assumed to have been killed in his cabin. This immediately narrows the suspect list down to five. A logical next step may be to search the cabins of those five suspects, to see what further connections I can turn up. Eventually, however, I will want to start questioning suspects. I can choose the approach I take to each. Various approaches are more or less favorable to different combinations of detective and suspect, something that must be deduced with play. If I choose wisely, perhaps I get a clue.
When I believe I have determined opportunity and motive (the game is oddly uninterested in the actual means of murder), I can accuse someone. A false accusation, or one based on insufficient evidence, doesn’t end the game, but does greatly affect your “detective rating” at the end, and prevents you from using that suspect as a source of information for the rest of the game. If you haven’t accused anyone by the time twelve hours (i.e., 36 minutes) have passed, you get one last chance to make an accusation, at some cost to your detective rating, before the game reveals the murderer for you.
There’s much that’s very impressive here. The randomly-generated cases go far beyond the likes of Colonel Mustard in the drawing room with the pistol. Most of the cases don’t even involve that most reliable standby of the mystery writer, love triangles. One time I discovered that Phillip Wollcraft, the archaeologist, had killed the young Natalia Berenski because he was in thrall to certain nameless be-tentacled somethings and needed a handy virgin to sacrifice. (Yes, even the H.P. Lovecraft mythos makes an appearance in this giddy pastiche of a setting, marking what may just be its first appearance in a computer game.) Another time I discovered that the beautiful pilot and all-around adventuress Stephie Hart-Winston had killed the Reverend Jeremiah Folmuth after learning he had in turn killed her beloved brother in a hit-and-run car accident years before. Other cases involve espionage (a natural given the time period), blackmail, even vampires. Most manage to tie the crime back to the period and setting and the specific persona of the characters involved with impressive grace.
But for all that, and despite its superficially easy joystick-driven interface and bright and friendly onscreen graphics that actually look much nicer (at least on the Atari) than those of Archon, Zinderneuf doesn’t quite work for me. Part of the problem derives from all of that rich background information existing only in the manual, not on the screen. The first half-dozen times you play you’re frantically flipping through the pages trying to figure out just who is who as the clock steadily ticks down, an awkward experience a million miles away from Trip Hawkins’s ethos for a new, more casual sort of consumer software. By the time you get over that hump, some of the seams in the narrative generator are already starting to show. You learn what combinations of clues generally lead where, and start to see the same motives repeat themselves. For all the game’s narrative flexibility, there are just eight master stories into which all of the other elements must be slotted. The shock of Wollcraft doing the deed diminishes considerably after you see the same story repeat itself again, with only the name of his victim changed. All of these limitations are of course easily understandable in light of the 48 K of memory the game has at its disposal. Still, things started feeling very shopworn for me long before Freeman’s ideal of a hundred plays.
I also found other elements of the design problematic. When you get down to it, there just isn’t that much to really do, and what there is is often more frustrating than it needs to be. Searching a cabin requires wandering about it trying to cover every square inch until the game beeps to inform you that you discovered a clue — or did not. And talking to suspects can be just as off-putting. Most will only answer a question or two before wandering off again; you then aren’t allowed to speak to them again without speaking to someone else first. Thus the game quickly devolves into a lot of sifting through denials and non-committals, struggling to figure out the right approach to use, while only being able to field one or two questions to your star witness (or suspect) at a time. The memory limitations so strangle the dialog that it’s impossible to pick up clues, as you might in a real conversation, about whether or why your current interrogation approach is failing, or which one might better suit. Murder on the Zinderneuf is fascinating and groundbreaking as a concept, but ultimately a game should be fun in addition to any other virtues it might possess, and here I’m just not sure how well it succeeds. Reading the manual with its cast of exaggerated characters was for me almost more entertaining than actually playing.
Zinderneuf‘s ideal of a narrative that is new every time is neat, and certainly interesting for someone like me to write about as the road almost entirely not taken in adventure games. But are there perhaps good reasons for it to be the road not taken? Maybe for someone primarily interested in games as experiential fictions a 40-hour story, crafted by a person, is more satisfying than 100 30-minute stories generated by the computer. At risk of making Freeman a straw man for my argument, it’s tempting to think again about the flaws that he believed he saw in existing adventures. I believe that designers who see games as rules systems to be carefully crafted and tweaked are often put off by adventure games, which are ultimately all about the fictional context, the lived experience of playing the protagonist in a story. Perhaps having the system itself generate the story could be seen, consciously or unconsciously, as a way to fix this perceived imbalance, to return the art of game design (as opposed to fiction-authoring) to the center of the equation. Yes, Murder on the Zinderneuf‘s narrative generator is clever, but it’s not as clever as, say, Marc Blank, the author of Deadline — and arguably not clever enough to sustain a genre whose appeal is so deeply rooted in its fiction. Zinderneuf is more interesting as a system than as a playable story, in a genre whose appeal is so rooted in story. That, anyway, is how this story lover sees it. Which isn’t to discount Zinderneuf‘s verve in trying something so new. We need our flawed experiments just as much as we do our masterpieces, for they push boundaries and give grist for future designers’ mill. (In that spirit, check out Christopher Huang’s An Act of Murder sometime, which does in text much of what Zinderneuf does in graphics, with results I find more satisfying.)
For several years after 1983, their landmark year of Archon and Murder on the Zinderneuf, Free Fall remained a prominent presence in the growing games industry. In 1984 they released Adept, a sequel to Archon that didn’t quite attract the same love or sales, but was nonetheless a solid success. Soon after they were given an early prototype of the Amiga, thanks to an arrangement Trip Hawkins, a great booster of that machine, worked out with Commodore. Their superb port of Archon became one of the first games available for the Amiga, and they followed it shortly after with a port of Adept of similar quality. Many players still consider these the definitive versions of both games.
Freeman also became a prominent voice in the emerging field of game-design theory, which was separating itself at last by the mid-1980s from the very different art of game programming. He, a defiant non-programmer who had written three books and numerous articles about the art of board-game design before founding Free Fall, was ideally suited to push that process along. Like the last designer I profiled, Dan Bunten, Freeman was given a soapbox of sorts via a column (“The Name of the Game”) in Computer Gaming World. Its ostensible purpose was to tackle tough, controversial subjects head-on. Yet there’s a thin line between delivering hard-hitting, unvarnished reality as one sees it and, well, just kind of sounding like a jerk, and I’m not sure Freeman always stays on the right side of it. His hilarious rant about the Commodore 64 proves that, whatever else he may be, he is no Nostradamus: “software developers will jump off the bandwagon even faster than they got on”; buyers “will think all computers are horrible and throw the whole idea out the window along with their 64.” The Commodore 64 has always evoked special rage from Atari 8-bit loyalists like Freeman. The Atari machines were the 64’s most obvious competitor as fellow low-cost home computers with excellent graphics and sound after weaker sisters like Texas Instruments left the market. They were also arguably the ones the 64 most damaged commercially. “There but for the 64 could have gone the Atari 8-bits,” Atari fans think when they see the 64’s huge success, and not without some justification. But Freeman’s, shall we say, strongly held opinions extended beyond the platform wars. Arcade clones are not just uncreative but morally bankrupt, “illegitimate,” “nasty little pieces of trash.” Programmers doing ports are people “who can’t come up with original subjects for games.” More generally, phrases like “colossal stupidity” and “I almost certainly know more — probably a lot more — about this than you do” creep in a bit too often.
Following the Amiga Archon ports, Free Fall worked for several years on a project that marked a return to Freeman’s roots with Automated Simulations and Temple of Apshai: Swords of Twilight, an ambitious RPG for the Amiga that finally appeared in 1989. It had the unique feature of allowing up to three players to inhabit its world at the same time, each with her own controller, adventuring cooperatively. Despite being released once again by EA, the game seemed to suffer from a dearth of distribution or promotion, and came and went largely without a trace, and without ever being ported beyond the Amiga, a relative minority platform in North America. Another five years elapsed before Free Fall released Archon Ultra, this time on the SSI label. That game was poorly received as adding little to the original, and once again sank quickly into obscurity. And, a few casual card games and the like aside, that’s largely been that from Free Fall. They are still officially a going concern, but seem to exist today largely to license their intellectual property (i.e., Archon) to interested developers. If their output after 1986 or so seems meager given the extraordinary productivity and energy of their first few years, know that my impression — and I must emphasize that this is only an impression, with little data to back it up — is that life has thrown its share of difficulties at Freeman and Westfall since their heydays as stars of Hawkins’s stable of software artists, difficulties that go beyond just some games that performed disappointingly in the marketplace.
If you’d like to try Murder on the Zinderneuf for yourself, I’ve prepared the usual care package for you, with an Atari 8-bit disk image and the (essential) manual. Next time we’ll say goodbye to EA’s Software Artists for a while and catch up with some Implementors again.
(A good interview with Freeman and Westfall can be found online at Halcyon Days, and one with Freeman alone at Now Gamer. Contemporary articles about Free Fall are in the January 1983 Softline, the November 1984 A.N.A.L.O.G., the February 1985 Family Computing, the July/August 1987 Info, and the November 1984 Compute!’s Gazette (Freeman must have been gritting his teeth through that interview, given his opinion of the Commodore 64). Freeman’s Computer Gaming World column ran from the May/June 1983 issue through the April/May 1985 issue.)